Chapter 18 Study Guide W/ans
advertisement

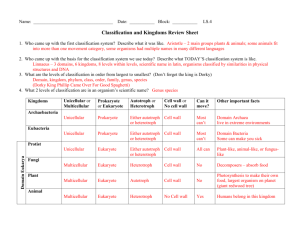
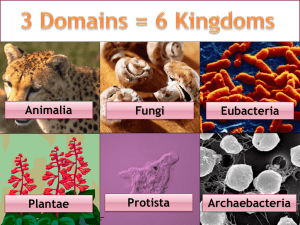
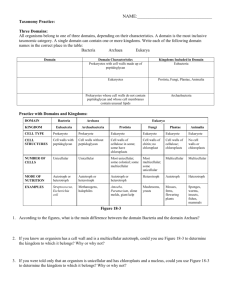
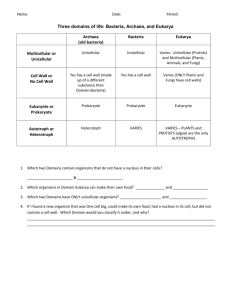
Completion terms AppearancesBinomialDNA EukaryaMoneraPhylum (used twice)scientific namespecies- 1. How do you know that the species Ursus maritimus and Ursus arctos are closely related? Yes they are because the have the same genus. Figure 18–1 2. Look at Figure 18–1. Why are such different animals as fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals grouped into a single phylum? They have similar structures such as a spinal chord. 3. If you know nothing else about an organism except its scientific name, can you immediately determine what genus and family it is in? Explain. No, you can determine the genus and species not the family. 4. Compare and contrast kingdom Fungi and kingdom Plantae in the six kingdom system. Plants have a cell wall of cellulose, where fungi have cell walls of chitin Figure 18–3 5. What characteristic is used to place an organism, such as the amoeba in Figure 18–3, in the domain Eukarya? It has a nucleus (eukaryote) Figure 18–4 Classification of Living Things DOMAIN Bacteria Archaea KINGDOM Eubacteria Archaebacteria Eukarya Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia CELL TYPE Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote CELL STRUCTURES Cell walls with peptidoglycan Cell walls without peptidoglycan Cell walls of cellulose in some; some have chloroplasts Cell walls of chitin Cell walls of cellulose; chloroplasts No cell walls or chloroplasts NUMBER OF CELLS Unicellular Unicellular Most unicellular; some colonial; some multicellular Most multicellular; some unicellular Most multicellular; some green algae unicellular Multicellular MODE OF NUTRITION Autotroph or heterotroph Autotroph or heterotroph Autotroph or heterotroph Heterotroph Autotroph Heterotroph EXAMPLES Streptococcus, Escherichia coli Methanogens, halophiles Amoeba, Paramecium, slime molds, giant kelp Mushrooms, yeasts Mosses, ferns, flowering plants Sponges, worms, insects, fishes, mammals Why don’t we use common names for organisms? What is Linnaeus’s system? What makes up a kingdom? Phylum? Class?.... The common name of animals will change from person to person or region to region. Linnaeus’s system of classification uses both small and large categories for classification A kingdom is made up of similar Phylum. A Phylum is made of similar classes, etc… What is binomial nomenclature? What are the two parts of binomial nomenclature and how do we write them? Binomial nomenclature is a two naming system in which the first name is the Genus and the second name is the species. It is written with Genus being capitalized and species not. What are Taxa? What is systematics? What is a monophyletic group? What is cladistics analysis? What is a derived characteristic? A taxa is a group or level of organization into which organisms are classified. Systematics is the study of the diversity of life and the evolutionary relationships between organisms Cladistic analysis is an analysis that focuses on the order in which derived characteristics appeared in an organism. A derived characteristic is a trait that appears in recent parts of a lineage, but not in its older members. What were the original two kingdoms? Why do we now have six? Plantae and Animalia. We now have 6 because of the diversity of organisms and the way we classify organisms. What are the differences between the three domains? Eukarya- are Eukaryotes Archaebacteria- unicellular prokaryotes that have cell walls that don’t have peptidoglycan. Bacteria- Unicellular prokaryotes that have a cell wall with peptidoglycan.