Ch. 5 section 2 cont

Section 1 cont.
Turgor pressure- the pressure that water molecules exert against the cell wall
Do the cells of this plant have turgor pressure?
Plasymolysis- when a plant doesn’t receive enough water and the cell membrane shrinks from the cell wall; turgor pressure is not maintained
Facilitated Diffusion
A type of passive transport that is used for
1) molecules too large to pass through the cell membrane
2) molecules that do not dissolve in lipids
Facilitated diffusion uses a carrier protein.
What might this molecule be?
Facilitated
Diffusion
1.
2.
3.
4.
Molecule attaches to protein.
Protein changes shape.
Molecule is released to other side.
Protein returns to original shape .
Ion Channels
Membrane proteins move Na+, K+, Ca +2 ,
Cl- across the cell membrane
Three kinds of stimuli determine whether “gates” are open:
1) stretching of the cell membrane
2) electrical signals
3) chemical signals
Section 2: Active Transport
-requires energy
-moves materials
up the concentration gradient (from low to high concentration)
The Sodium-Potassium Pump
Moves 3 sodium (Na) out and 2 potassium
(K) in…
Since there’s already more sodium on the outside, energy is required…
It’s like bailing water out of a boat that continues to fill
The sodiumpotassium pump moves 3 positive ions out for every 2
Hmmm… positive ions in; which side of the cell membrane is slightly more negative than the other??
The inside…
The inside of a cell (like a nerve cell) is slightly more negative than the outside
This electrical gradient (difference in charges) enables impulses to be sent along nerve cells
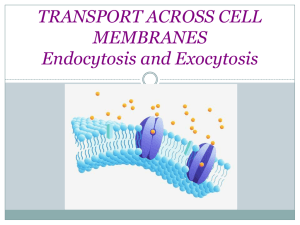
Movement in Vesicles
Endocytosis
Two types:
A. pinocytosis- a cell takes in fluids or solutes
B. phagocytosis- a cell takes in large particles or whole cells
Exocytosis
A process by which a substance is released from a cell
- toxins
-proteins
-waste products
Endocytosis
A color-enhanced transmission electron micrograph of an amoeba engulfing green algal cell for food.
An amoeba and endocytosis…
Many unicellular organisms feed by phagocytosis…
Phagocytes
-Your white blood cells ingest bacteria and viruses
Exocytosis