Biology
advertisement

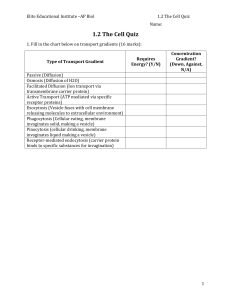
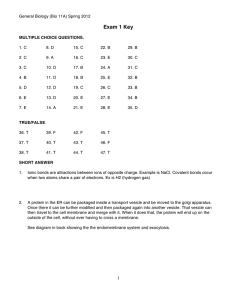
Biology Movement Through Cell Membranes – Chapter 5.4 1. Define the following terms: Passive transport – Concentration gradient – Equilibrium – Osmosis – Facilitated diffusion – 2. Label the following cases as hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic. 3. If left unchecked, the swelling caused by a hypotonic solution will cause a cell to _____________________. 4. Transport proteins called _______________________ provide polar passageways through which ions and polar molecules can move across a cell membrane. 5. An ____________________________________ is a doughnut-shaped transport protein with a polar pore through which ions can pass. 6. Name two influences on the rate of movement of a substance across a cell membrane. a. b. 7. Name one instance where the ion’s electrical charge often affects the diffusion of the ion across the cell membrane. 8. Define: facilitated diffusion – carrier protein – 9. Why are green leafy vegetables sprinkled with water at the supermarket? 10. Why is salt sometimes used to preserve foods? 11. Why should you not drink sea water? Active Transport 12. Define: Active transport – Endocytosis – Exocytosis – Pinocytosis – Phagocytosis – 13. How does active transport differ from passive transport? 14. How does a membrane pump work? 15. Describe the four (4) steps in the sodium-potassium pump. a. b. c. d. 16. Some substances are too large to be transported by carrier proteins and are moved across the cell membrane by _______________________. 17. The movement of a substance INTO a cell by way of a vesicle is called ____________________________. 18. The movement of a substance OUT OF a cell by way of a vesicle is called __________________________. 19. Describe two instances where substances are moved out of the cell by exocytosis. a. b.