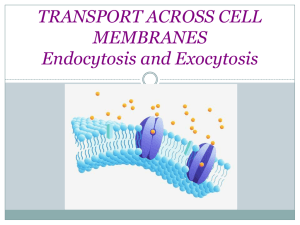
Endocytosis and exocytosis
advertisement

A Closer Look at Cell Membranes Aim: How do large particles enter and exit cells? Do Now: Name some molecules/materials that enter and exit the cell. How would you describe the cell membrane that allows passage of these materials? Exocytosis and Endocytosis Exocytosis (out of the cell) • The fusion of a vesicle with the cell membrane, releasing its contents to the surroundings Endocytosis (into the cell) • The formation of a vesicle from cell membrane, enclosing materials near the cell surface and bringing them into the cell Endocytosis and Exocytosis Examples Three Pathways of Endocytosis Bulk-phase endocytosis • Extracellular fluid is captured in a vesicle and brought into the cell; the reverse of exocytosis Receptor-mediated endocytosis • Specific molecules bind to surface receptors, which are then enclosed in an endocytic vesicle Phagocytosis • Pseudopods engulf target particle and merge as a vesicle, which fuses with a lysosome in the cell Phagocytosis (“engulfment”) Membrane Cycling Exocytosis and endocytosis continually replace and withdraw patches of the plasma membrane New membrane proteins and lipids are made in the ER, modified in Golgi bodies, and form vesicles that fuse with plasma membrane Exocytic Vesicle 5.5 Key Concepts: Membrane Trafficking Large packets of substances and engulfed cells move across the plasma membrane by processes of endocytosis and exocytosis Membrane lipids and proteins move to and from the plasma membrane during these processes