Cellular Transport - stephaniemcoggins
advertisement

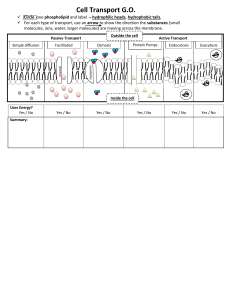
Cellular Transport The Cell Membrane • Remember: ALL cells have a cell membrane! • Remember its function: To act as a boundary between the inside of the cell and the outside of the cell. It protects the cell by keeping the good things in and the bad things out! • This boundary maintains an internal balance in the cell called HOMEOSTASIS. • The cell membrane has holes in it, like how our skin has pores. This is called being SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE. It allows some things in and keeps other things out. Types of Cellular Transport • Passive Transport- the cell does NOT use energy 1. Diffusion 2. Osmosis • Active Transport- the cell USES energy 1. Endocytosis 2. Exocytosis Passive Transport • The cell uses NO energy • Molecules spread from an area of HIGH concentration to an area of LOW concentration Weeee!!! • HIGH LOW high low PASSIVE TRANSPORT Diffusion and Osmosis • Diffusion is movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. • Molecules continue to spread out until equilibrium is reached. • Osmosis is simply diffusion of WATER across a membrane. Active Transport • The cell USES ENERGY • Molecules spread from an area of LOW concentration to an area of HIGH concentration • LOW HIGH high low This is gonna be hard work!! ACTIVE TRANSPORT Endocytosis • Uses energy! • The cell engulfs something outside of it and takes it INTO itself. • This is how white blood cells eat bacteria! • VIDEO ACTIVE TRANSPORT Exocytosis • Uses energy! • FORCES material outside of the cell • This is how hormones or wastes are released from the cell • VIDEO