Introduction to membrane transport
advertisement

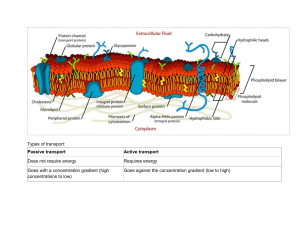
Introduction to membrane transport The cell membrane is SEMIPERMEABLE: some substances can move across the cell membrane while others can’t. • Concentration gradient: a difference in concentration between one side of the membrane and the other • Processes that allow substances to move across the membrane without energy are PASSIVE TRANSPORT. They use the concentration gradient • Includes diffusion, osmosis and facilitated diffusion Active transport • Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient • Requires energy (in the form of ATP) • Includes active transport, and membraneassisted transport (endocytosis and exocytosis)