Colonial Review Slideshow
advertisement
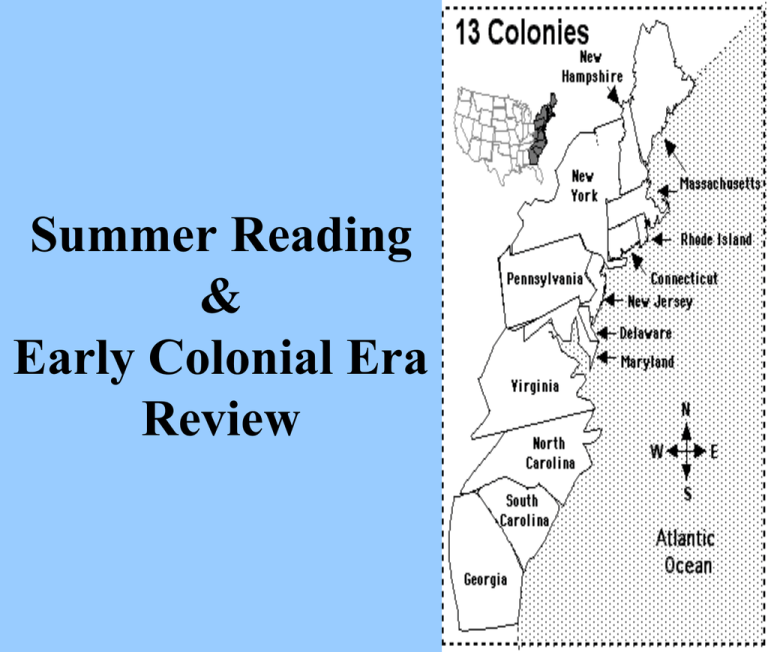
Summer Reading & Early Colonial Era Review Common motivations for all European Exploration in the New World • Power & Prestige • Profit • Religion Purposes of the Colonies • Profits • Raw Materials/Columbian Exchange • Mercantilism The Creation of Colonial Identity, 1607-1763 1. Economic: Salutary Neglect, South Atlantic System 2. Geographic: Regional Diversity 3. Intellectual: Enlightenment & Great Awakening What made the Northern Colonies unique? • New England: – Massachusetts – New Hampshire – Rhode Island – Connecticut Puritan Society • “Theocracy” led by Gov. John Winthrop - “City Upon A Hill” • Results of Puritans? • How did the religious dissenters who founded New England deal with dissent within their own sect? Political Independent Spirit of New England Established What made the Middle Colonies unique? • • • • New York Pennsylvania New Jersey Delaware Tolerance in Middle Colonies • Most diverse backgrounds & religions • Most tolerant What made the Southern Colonies unique? • Chesapeake – (Maryland, Virginia) • Lower South – (North Carolina, – South Carolina, Georgia) Laborers & Landowners • “Headright” system • Indentured Servitude vs. Slavery • Yeoman Farmers vs. Landed Gentry British-Native Relations in Chesapeake • Why would lower class farmers follow the wealthy Nathaniel Bacon into rebellion against the local aristocracy? • Results of Bacon’s Rebellion? Colonial Cultural/Intellectual Changes by Mid 1700’s Demonstrate “Alternative” Thinking in the Colonies • 1st Great Awakening • Old Lights vs. New Lights • Revivalism • New Denominations • Enlightenment • Deism • Franklin











