Units 1 and 2
advertisement

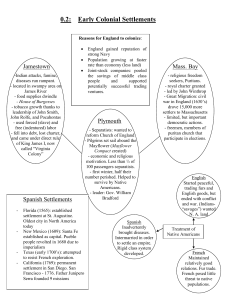
units 1 and 2 exam preparation assignment Directions: This assignment is offered as a way to prepare for Friday’s unit exam. Please complete each of the following steps. Reviewing the Terms: Highlight the following based on innovation, power, and conflict and change. Christopher Columbus Columbian Exchange Conquistadores Encomienda system “black legend” Herńan Cortés Treaty of Tordesillas Robert de la Salle Vasco da Gama “Mission Indians” Mestizos Marco Polo Francisco Pizarro John Rolfe Walter Raleigh James Oglethorpe John Smith primogeniture Virginia Company Jamestown [what struggles did it face?] Pocahontas Maryland Act of Toleration joint-stock company slavery House of Burgesses Lord Baltimore Humphrey Gilbert Oliver Cromwell royal charter slave codes proprietary colony Sir Francis Drake Spanish Armada Restoration Period Iroquois Confederacy squatter yeoman Pilgrims Separatists Protestant Reformation Mayflower Compact Mayflower Puritans enclosure John Calvin Anne Hutchinson Roger Williams Henry Hudson William Bradford patroonship Bible Commonwealth Quakers Calvinism Peter Stuyvesant Thomas Hooker William Penn Separatists doctrine of a calling “visible saints” conversion Great Puritan Migration Institutes of the Christian Religion John Winthrop “city upon a hill” King Philip John Cotton Sir Edmund Andros the “elect” Fundamental Orders of Conn. covenant antinomianism Navigation Laws New England Confederation Protestant ethic Massachusetts Bay Company William Laud headright system jeremiads town hall meetings middle passage indentured servitude Half-Way Covenant Nathaniel Bacon Bacon’s Rebellion William Berkeley Stono Rebellion The Great Awakening Jonathan Edwards Benjamin Franklin Paxton Boys George Whitefield Regulator movement Phyllis Wheatley “old” and “new” lights Molasses Act Big Ideas 1. Provide evidence in support of each of the following themes. The “collision of worlds” and the effects on societies on both sides of the Atlantic Encounters with Indians and African slaves established the patterns of race relations that would shape the North American experience Principles of American government developed in New England with the beginnings of written constitutions (Mayflower Compact and the Massachusetts royal charter) Self-rule seen in town hall meetings, the New England Confederation, and colonial opposition to the Dominion of New England Colonial culture, while still limited, took on distinct American qualities in such areas as evangelical religion, education, press freedom, and self-government Regional differences throughout the colonies, from the emergence of the industrial north and the growth of the plantation economies and slave societies of the south The rise of colonial culture and the development of a distinct American identity For each of the following lists, be sure to provide specific historical evidence to support your selections. 2. What events, actions or policies in England’s American colonies helped to foster religious or political equality? What events, actions or policies in England’s American colonies resulted in limited political or religious equality? 3. Rank the 5 most significant religious, economic or political conflicts in the English colonies in America.