Psychological Research Methods & Statistics Notes
advertisement

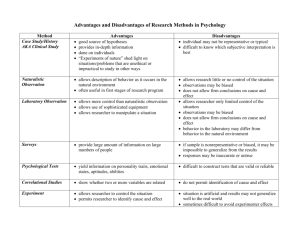
Name _________________________________ Date _________________________ Period ___________ Psychological Research Methods and Statistics Notes Part 1 Pre-Research Decisions: 1. Form a research question 2. Select a research method 3. Identify the sample Sample – the ___________ group of participants, out of the total number available, that a researcher studies - Must be representative of the population a researcher is studying. - How to avoid a nonrepresentative sample: o Random sample – each individual has an ___________ chance of being selected Ex: Drawing names or every 20th person o Stratified sample – subgroups in the population are represented proportionally Ex: School children – gender, race, age Methods of Research Naturalistic observation – research method in which the psychologist observes the subject in a natural setting without interfering - Example: Jane Goodall observing chimps in the wild daily Case study – research method that involves an intensive investigation of one or more participates (long-term) o Results are __________ to the individual and cannot be generalized to anyone else. o Provide descriptive information that can generate new hypotheses. Survey – research method in which information is obtained by asking many individuals a fixed set of questions o Interview, questionnaires, or a combination What are the benefits of using an interview? What are the benefits of using a questionnaire? Longitudinal study – Research method in which data is collected about a group of participants over a ______________________________to assess how certain characteristics change or remain the same during development Good for examining consistencies and inconsistencies in behavior over time. Ex: NY Longitudinal Study beginning in 1956 o Followed 133 infants to adulthood. o Discovered that children are born with different temperaments. Cross-sectional study – research method in which data is collected from groups of participants of different ages and compared so that conclusions can be drawn about differences due to age. o Why could this study be better than a longitudinal study? Correlation- the measure of a ______________________ between two variables or sets of data o Ex: There is a positive correlation between IQ scores and academic success. o Ex: There is negative correlation between the number of hours you practice shooting free throws and the number of times you miss. o Correlation is NOT cause and effect. Experiments o Why would a researcher choose experimentation over the other research methods? o Hypothesis - an educated guess about the relationship between two variables What you expect to find. Variable – any factor that is capable of ___________________ Independent variable – the one that experimenters change or alter so they can observe its effects. Dependent variable – the one that changes in relation to the independent variable. Ex: The number of hours you study (independent v.) affects your performance on an exam (dependent v.) o Experimental group- the group to which the __________________ variable is applied. o Control group – the group that is treated is treated in the same way as the experimental group except that the experimental treatment (the independent variable) is not applied. Ethical Issues Ethics - methods of conduct or standards for proper and responsible behavior.