Research Design
advertisement

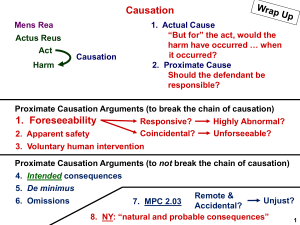
Research Design Purposes for Research Criteria for Causation Units of Analysis The Time Component Three Purposes of Research • Exploration • Description • Explanation Criteria for Causation • Two Things Must be Related (Correlation) • The Cause Must Precede the Effect (Time ordering) • The Relationship Must be “Non-Spurious” Common Mistakes • “Complete” causation • Exceptional cases • Majority of cases Necessary / Sufficient • A Necessary Cause – X must be present for Y to occur • A Sufficient Cause – If X is present, Y must occur Units of Analysis • This is the “what” that is being studied – Social scientists can have almost anything as the unit of analysis – It is even possible to have a study with multiple units of analysis • Be CAREFUL – Knowing that a person studied “people” does not necessarily tell you the unit of analysis Some of my tricks… • Look at what a researcher is predicting or counting—if something is expressed in “rates,” it is a group level unit of analysis • Rephrase a persons research hypothesis or statement in way that makes the unit of analysis more explicit • If “groups” are a part of the study, figure out whether the researcher is comparing groups, or simply using group status as an “attribute” in order to compare individuals The Individual Level • Typically, individual people – Don’t confuse “generalizing” with units of analysis – You can study “groups” or “classes” of people, but still have individuals as unit of analysis • Non-people examples – Social artifacts and Social interactions • Typically individual, but could be aggregates Group (Aggregate) Level • KEY = the group is the entity we study— looking at attributes of the group – May sometimes studies individuals to construct such attributes (e.g., construct rate) • Organizations – Corporations, churches, TIME • Why is “time” important? – Causal ordering – Generalization • Cross-Sectional Research • Longitudinal – Trend – Cohort – Panel Ways to Get Around Longitudinal Research (e.g., Cheating) • Logic can sometimes dictate cause and effect • Sometimes the data can help draw conclusions about cause and effect • Retrospective studies • Use age differences within sample to reach conclusions • Repeat a prior cross-sectional study Designing a Research Project • Research is MESSY!!! • Theories and Ideas • Starting Point – Read, read, read – Purpose of research • Conceptualization • Choice of Research Method