Psychology Research Methods: An Overview
advertisement

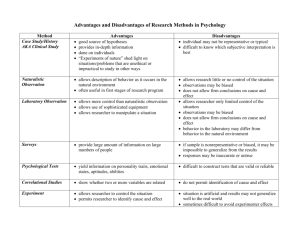
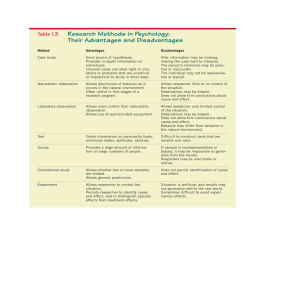
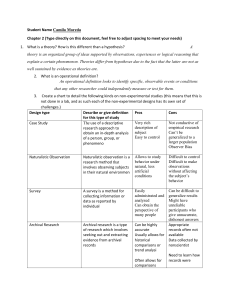
Psychology Research Methods Tuesday: Bring Headphones!! Sample The small group of participants, out of the total number available that a researcher studies. Naturalistic Observation Method in which psychologists observe the subject in a natural setting without interfering. Examples : Jane Goodall Case Study Method that involves an intensive investigation of one or more participants. Example: Freud Surveys Method in which information is obtained by asking many individuals a set of fixed questions. Example: Voting Projections Longitudinal Study Method in which data is collected about a group of participants over a number of years to assess how certain characteristics change or remain the same during development. Example : Mr. Hannah follows you to college Cross-Sectional Studies Method in which data is collected from groups or participants of different ages and compared so that conclusions can be drawn about such differences due to age. Tracking learning abilities at different ages. Experimentation Researcher controls the situation to analyze samples. Example : Creating a simulation of a fight to test the bystander theory. Some Experimentation Terms Self-fulfilling prophesy Situation where a researcher’s expectations influence the sample’s behavior, making an inauthentic experiment. Examples: Counting horse, Inkblots Single-Blind Experiment Experiment where the participants are unaware of which participants received the treatment. Example: Milgram Experiment Double-Blind Experiment An experiment which neither the experimenters nor the participants know which participants received the treatment. How could this be more authentic than a single blind experiment? Placebo Effect A change in a participant’s illness or behavior that results from a belief that the treatment will have an effect, rather than the actual treatment. Reflection Which research method do you think is best? (naturalistic observation, survey, case study, experiment, longitudinal, cross-sectional)