Carbohydrates & Lipids
advertisement

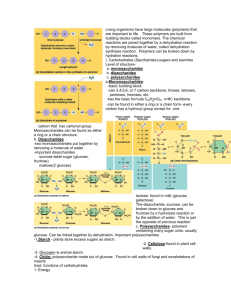
• The individual pieces that make them are called monomers. – – – – 2 monomers make a dimer 3 make a trimer ... many together form a polymer Roughly 40 - 50 different monomers combine to make up the thousands of different macromolecules present in the cells. • The 4 main classes are: lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids. – Can be formed through a condensation reaction called dehydration synthesis – Can be separated through hydrolysis Macromolecules Carbohydrates • Carbohydrates are sugars. Sugars can be single units which are monosaccharides (simple sugars), as disaccharides, or as long chains which are polysaccharides. • Each monosaccharide is added through the process of dehydration synthesis forming a glycosidic linkage Monosaccharides • monos - single, sacchar – sugar… Often called simple sugars – empirical formula of (CH2O)n – Molecular formula C6H12O6 (Glucose) • contains a carbonyl group and multiple hydroxyl groups • end is suffix -ose – aldose sugar…end carbonyl unit – – ketose …middle carbonyl unit • forms a hexagonal ring (hexose), other common rings are triose and pentose • Glucose, Galactose, & Fructose are common isomers Common Disaccharides • Disaccharides are formed through the process of dehydration synthesis. – They are important as they are small enough to be absorbed intact through the small intestine directly into the bloodstream – Can be easily cleaved to release glucose to support metabolism • Starches are the polysaccharide storage form of the simple sugars found in the body – Starch is stored by plants – Glycogen is a branched polysaccharide stored in the muscles of animals • Both starch and glycogen are made exclusively of glucose, in an alpha arrangement, and can be used to release glucose into the circulatory system when the blood sugar drops – Cellulose is a structural polysaccharide much like starch but the orientation is a beta pleat causing a more condensed packaging that gives strength, support, and makes the molecule indigestible to most organisms – Chitin is a structural polysaccharide produced by arthropods to build exoskeletons Starches • Hydrophobic molecules formed by dehydration synthesis creating ester linkage – Made of glycerol (3C alcohol) and fatty acids (long hydrocarbon chains) – Triglyceride is the most common form consisting of a glycerol and 3 fatty acids Lipids (fats) • • • A saturated fat has fatty acids containing no double bonds…it is holding as many H as possible An unsaturated fat has at least 1 double bond (monounsaturated) A polyunsaturated fatty acid contains many double bonds Saturated vs Unsaturated Phospholipids and Steroids • Phospholipids are a major component of cell walls. – Are a diglyceride with a phosphate molecule creating a hydrophilic and hydrophobic end • A steroid is a derivative of cholesterol and is used as a chemical messenger in animals