Functional Groups
advertisement

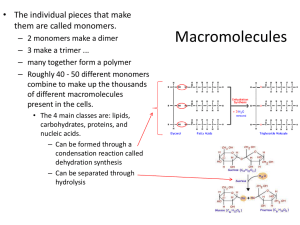
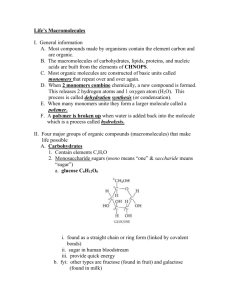
Functional Groups Functional Groups Functional groups are groups of organic molecules that react in predictable ways We use them to understand biochemical reactions between carbohydrates, fatty acids, proteins and nucleic acids Condensation reactions dehydration synthesis Take a look at the reaction drawn here Name the functional groups involved This is a reaction that bonds two glucose molecules together and produces maltose and water Dehydration synthesis between two hydroxyl groups Hydroxyl groups characterize alcohols and sugars They are polar and participate in the the synthesis reactions that build starches from simple sugars This diagram continues where the previous one left off - the synthesis of maltose from two glucose molecules Dehydration synthesis of sucrose In this example, one glucose is replaced with fructose The reaction is the same though, because the functional groups are both hydroxyl - like the 2 glucose molecules Carbonyl groups Carbonyl groups are also polar They can be found at the end of the carbon chain, or in the middle They are characteristic groups in ketones and aldehydes Simple sugars contain polar carbonyl groups they are either ketose sugars (fructose) or aldose sugars (glucose) Carboxyl Groups These polar groups are characteristic of organic acids They are particularly important to fatty acids the long carbon chains are unreactive and nonpolar, but dehydration synthesis reactions can occur at the functional group end Amino Groups Amino groups are basic and polar and characterize amino acids, the building blocks of protein What is the second functional group that characterizes amino acids? Amino acids and peptide bonds These two groups are critically important in the formation of proteins Peptide bonds form between the two functional groups another example of dehydration synthesis Phosphate groups and sulfhydryl groups Phosphate groups are responsible for bonding with hydroxyl groups in the backbone of DNA molecules Sulfhydryl groups react with each other, forming covalent bonds in proteins