10/5/2011 1 Objectives Overview A. Inorganic compounds 1. Water
advertisement

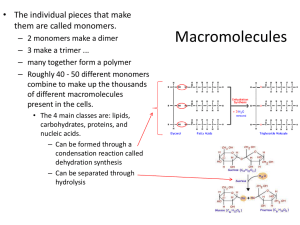
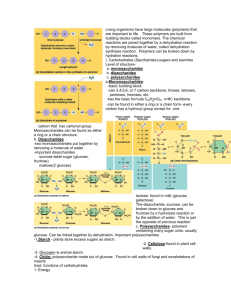
10/5/2011 Objectives 1. 2. 3. Distinguish organic from inorganic compounds Explain the importance of water to the body Differentiate a salt, an acid and a base Biochemistry Chapter 2 Bell Ringer: What is the major function of potassium in the body? Overview A. Inorganic compounds All Lack molecules in the body are either inorganic or organic carbon simple molecules Small, Examples: water, salts and acids and bases 1. Water 2. Salts 2/3 Ionic the body’s weight Properties: High heat capacity- prevents sudden body temp changes Polarity/solvent properties- helps chemical reactions occur, dissolves nutrients, wastes and lubricates Chemical reactivity- major reactant Cushioning- fluids that protect the body compounds in water Ca and P salts most abundant Are all electrolytes (conduct electrical current in solution) Dissociate 1 10/5/2011 3. Acids 4. Bases Also Also Substance Substances electrolytes that can release hydrogen ions, H+ (proton donors) and anions Examples: HCl, acetic acid, carbonic acid electrolytes that can release hydroxyl ions, OH- (proton acceptors) and cations Example: bicarbonate (HCO3-) Neutralization reaction- acids and bases react to form salt and water Objectives Importance of pH 4. Explain the importance of pH to the body 5. Define carbohydrates in terms of their building blocks, structures and functions in the body pH of 7 is neutral (hydrogen ions = hydroxyl ions) pH below 7 is acidic (> hydrogen ions) pH above 7 is basic (> hydroxyl ions) Bell ringer: List 4 important roles of water in the body and provide an example of each. pH of the blood B. Organic compounds Narrow Carbon If Large range (7.35 to 7.45) pH is not stable death can occur Example: if blood becomes slightly acidic hemoglobin cannot carry oxygen Regulated by kidneys, lungs and buffers (weak acids and bases that take up excess ions) containing compounds covalently bonded molecules Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids 2 10/5/2011 1. Carbohydrates Functions Sugars Source and starches C, H and O Ratio- 2H to 1O Classified according to size (monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides Building block: monosaccharides Contain of food energy for cells (ATP from oxidation of glucose) Excess converted to glycogen or fat and stored Used for cell structure Found in genes (ribose, deoxyribose) Guide cellular interactions Structure Monosaccharides (simple sugars) to 7 carbon atoms (single ring) Glucose, fructose, galactose Ribose and deoxyribose 3 Disaccharides Disaccharides in the diet Two Sucrose simple sugars joined by a synthesis reaction Dehydration reaction (a type of condensation reaction) – water molecule lost as the bond forms Bond between sugars is a glycosidic linkage Hydrolysis- bond is broken when water molecule is added ( glucose + fructose)- cane sugar (glucose + galactose)- milk Maltose (glucose + glucose) – malt Lactose These must be broken down to be absorbed by the blood 3 10/5/2011 Polysaccharides Objective Long, branching chains of simple sugars insoluble, not sweet Used for storage Starch (plants)- grains and root vegetables Glycogen (animals)- muscle and liver 6. Define lipids in terms of their building blocks, structures and functions in the body 2. Lipids Triglycerides Large Function: Large, molecules, insoluble in water C, H and O but many H atoms compared to O Triglycerides, phospholipids and steroids Found in meat fat, eggs, milk products and oils Contain Bell Ringer: What molecule in animals is a major storage of carbohydrates? concentrated source of usable energy Stored in fat deposits beneath skin and around organs Protect from heat loss and “bumps” Termed “neutral fats” 4 10/5/2011 Structure Types Building Saturated blocks: glycerol + 3 fatty acids depends on length of fatty acid chains and types of bonds between carbons Solidity – single covalent bonds between carbons (solid) Animal fats, tend to have long chains Unsaturated- double or triple bonds between carbons (oils) Plant oils, shorter chains Trans fats- oils that have been solidified by adding H atoms • Still formed by dehydration reaction and broken by hydrolysis • Bond formed is an ester bond A monounsaturated triglyceride Phospholipids Similar to triglycerides phosphorus containing group takes the place of one of the fatty acid chains Makes a polar head (slightly charged)and a tail Phosphorus “head” interacts with water (hydrophilic) and ions but fatty acid “tail” does not (hydrophobic) Found in cell membranes A 5 10/5/2011 Steroids Flat molecules, 4 interlocking rings Fat-soluble Cholesterol most important Found in cell membranes and needed to make Vitamin D, steroid hormones and bile salts Some made in liver and ingested from animal products Review questions What are the three basic monosaccharides? What type of lipid contains three fatty acid chains and a glycerol? What is the most common steroid? What are the fat soluble vitamins? 6