Review for Matter
advertisement

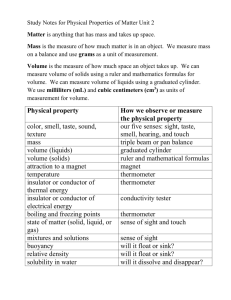
Review for Matter Test Matter Anything that has mass and takes up space All objects are made up of matter! Mass Mass measures the amount of matter that makes up an object. Mass will never change!! Only weight will change. Use a pan balance or triple beam balance to find the mass of an object in grams or Kilograms. Volume The amount of space that matter takes up. Examples: Popped popcorn has a higher volume than unpopped popcorn. Finding the volume of an irregular object 1. Observe and record the water level in graduated cylinder. 2. Drop your item into the graduated cylinder. 3. Record/observe the new water level. 4. Subtract the two water levels and you will find the item’s volume in cm cubed or mL. Volume of a regular shaped object Multiply the length X width X height to find volume. Density Density is the amount of mass in a given volume of matter. It is a property of matter that compares an object's mass to its volume. When an object is less dense, it will float. When an object has a higher density, it will sink. States of matter The form in which particles are arranged in different ways and move. Matter exists in three states-solid, liquid, and gas. The phase changes is the process of matter in one phase changing into another phase. Solids Particles in solids move the slowest. A solid has a definite shape and takes up a definite amount of space. Particles are close together and vibrate in place. How a solid changes: A solids heats up to become a liquid, and it gains energy. Liquids A liquid does not have a definite shape, but it takes up a definite amount of space. Particles are arranged close together, but not in a pattern. The particles slip and slide past each other. How a liquid changes: A liquid cools off to become a solid, and it will lose its energy. It heats up to become a gas, and gains energy. Gas Gas does NOT have a definite shape and does NOT take up a definite amount of space. Particles in a gas are far apart and move in all directions. Gas particles move the fastest out of all the states of matter. How gas changes: When cooled off, a gas becomes a liquid. It will lose energy once it becomes a liquid. Energy and states of matter When you apply heat, you are increasing the energy in a state of matter. When you take away heat and a state of matter cools off, it loses energy. Melting Point Melting in the process/temperature of changing a solid into a liquid. Evaporation Evaporation is the process of changing a liquid into a gas Example: Leaving a mixture of sugar and water out in the sun. The water evaporates, and the sugar is left over. Condensation Condensation is the process of changing a gas into a liquid Example: In clouds, water evaporates as a gas and then condenses into water droplets. Freezing Freezing is the process of changing a liquid into a solid. The freezing point of pure water is 0 degrees Celsius. Boiling Point The boiling point of pure water is 100 degrees Celsius. The boiling point is the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas. Mixture A combination of 2 or more substances where substances can be easily separated. Example: Cheerios and gummy bears. You can take out the gummy bears. Solution A solution is where one or more substances are dissolved in another substance. Example: salt and water mixed together. The salt will dissolve into the water. In order to separate the salt from this solution, let the water evaporate. Filtration Filtration is the process of separating substances with a filter. Example: Using a magnet to separate paper clips from marbles. Melting Point The melting point is the temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid. Properties of Matter A property is a characteristic of an object. Matter can be measured by : mass, weight, temperature, volume, size, and density Properties that you can sense: shape, color, texture, taste, state Matter can also have a magnetic quality.