Diseases Overview Power Point communicable
advertisement

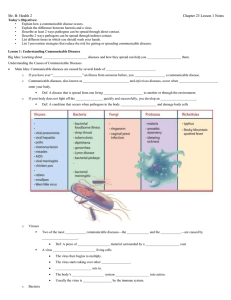
Communicable Diseases Edmonds School Dist. 15 Health Text Book Page 620 (answer in journal) • Define – communicable disease, viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoans & rickettsias • How are they transmitted? • How can you prevent? • Page 637 – Read the information on Hepatitis. Describe what this disease does to the body and explain the difference between A, B & C. Communicable: • Caused by direct or indirect spread of pathogens from one person to another. They enter and multiply within the human body. Causes • Bacteria (single cell microorganism) – They enter the body and multiply rapidly through cell division. Can live anywhere – air, soil, water – some produce toxins. • Viruses (genetic material coated by protein) – Are not living cells but attach themselves to living cells (hosts) and injects its genetic material into that cell, makes copies and spreads to other cells Causes continued • Rickettsias (similar to bacteria) – Most are found in the intestinal tracts of insects (fleas, ticks, mites and also mice) and are passed through bites or through feces deposited on the skin. • Fungi (plant like organisms) – Ring worm or athletes foot. They prefer dark, damp environments and invade deep tissue like hair, nails and skin. How are communicable diseases spread? • DIRECT CONTACT – People, Animals or Environment • INDIRECT CONTACT – Contaminated objects – table, door handles, eating utensils, tooth brush, needles, etc. – Vectors (flies, mosquitoes & ticks) – transfers pathogens from person to person – Water & Food Prevention • • • • • • • Wash hands Food Handling Strong Immune System No Sharing (utensils, make up, combs etc) Contact with people, etc. Stress….. Immunizations Bodies Means of Preventing Communicable Diseases • Physical barriers (skin, mucus, cilia etc) • Chemical barriers (enzymes in saliva and gastric juices) • Immune System Response – Inflammatory Response – Antigen – substance that is capable of triggering an immune response Types of Communicable Diseases • • • • • • • • • Cold and flu Tuberculosis (affects lungs) Strep Throat Encephalitis (inflammation of the brain) Meningitis (inflammation of the membranes that cover the brain) Polio (impacts the CNS causes paralysis) Measles (cold, fever, rash) Mono (fatigue, swollen glands) Hepatitis (inflammation of the liver)A, B & C