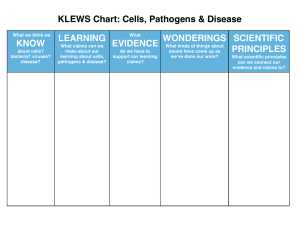
what are communicable diseases
advertisement

What Are Communicable Diseases? WHAT IS THE BEST WAY TO PREVENT SPREADING COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Communicable disease: A disease that is spread from one living thing to another or through the environment. Causes of Communicable Diseases Pathogen An organism that causes a disease Common pathogens…. viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoans, and rickettsias Infectioncondition that occurs when pathogens enter the body, multiply, and damage body cells Disease develops Viruses Pieces of genetic material surrounded by a protein coating The nuclear (chromosomal) and cytoplasmic (mitochondrial and chloroplast) material that plays a fundamental role in determining the nature of all cell substances, cell structures, and cell effects; the genes have properties of self-propagation and variation. Alone they are inactive Need living cells to produce Includes all forms of life Once inside a host cell virus makes more viruses Viruses usually kill the host cell and take over other cells Usually “run their course” Antibiotics do not work Common viruses Common cold, flu, AIDs, chicken pox, measles Bacteria Single-celled microorganisms- are everywhere! Some harmless Some helpful- in digestive system they help digestive food and certain vitamins When inside your body they multiply- cell division Some bacteria produce toxin- kills cells or interferes with their functions Tetanus- Infection generally occurs through wound contamination and often involves a cut or deep puncture wound Bacteria and viruses can be killed by immune system Most bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics Common: Strep throat, lyme disease, tuberculosis, Fungi Plantlike organisms Molds and yeast Disease of skin, mucosal membrane, or lungs Athlete’s foot Protozoans Single-celled organisms larger and more complex than bacteria Most are harmless Some can cause disease especially in people with weakened immune systems Rickettsias Similar to bacteria Often from insect bites (fleas and lice) Rocky Mountain Fever most common How They are Transmitted Direct Contact Touching, biting, kissing, and sexual contact Sneezing or coughing- sprays infected saliva or mucus Mother transmits infections to unborn child Indirect Contact Contaminated object germs move onto an object- someone touches the object and picks up the germs Examples.. Wash hands to prevent picking up infections Vectors An organism that carries and transmits pathogens to humans or other animals Examples.. Mosquitoes- malaria, Ticks- Lyme disease Water and Food Carless handling, cooking, and storage of food Water contaminate with pathogens Airborne Transmission Pathogens travel in the air from a sneeze or cough Long distances Chicken pox, influenza, tuberculosis Preventing the Spread of Disease Washing Hands Most effective way to prevent spread of disease When…. Before preparing food and eating After the bathroom Before contacts After touching animals When around an infected person Handle food properly Cook properly Chill leftover to proper temp Separate raw meat from other foods Other Measures Eat balanced diet Avoid use of drugs Avoid eating and drinking after people Avoid contact with infected people Keep vaccines up to date Manage stress