B. Immune System – Fighting to Stay Healthy
advertisement

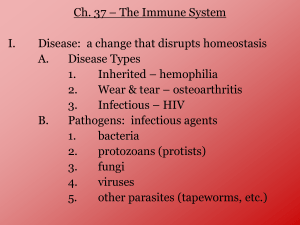
Connect! • Have you ever had… the measles? the mumps? a cold? the flu? • Why/why not? • What words come to mind when you see the term “Immune System”? B. Immune System – Fighting to Stay Healthy Homeostasis is constantly threatened by disease Inheritance Toxins Causes of Disease Unhealthy Lifestyle Risky Behaviors Pathogens ♦ the immune system which consists of lymph, mucus, lymph nodes, and white blood cells allows us to effectively combat invaders Pathogens (the bad guys) There are many potentially dangerous disease-causing organisms called pathogens in our air, water, and food such as 1. Viruses *composed of a nucleic acid and a protein coat *spread easily *examples include common cold, flu, and chickenpox 2. Bacteria *one-celled organisms *some bacteria cause illnesses such as strep throat, syphilis, and food poisoning 3. Fungi *organisms that eat by absorbing food *examples include athlete’s foot fungus and ringworm 4. Parasites *include animals and one-celled organisms that live and feed on other organisms *examples include leeches and tapeworms chunk! • Name 5 causes of disease. • What are the parts of the immune system? • What is the job of the immune system? • Define pathogen. • Name 4 types of pathogens. • Give characteristics and examples of each type of pathogen. Fighting the Pathogens All cells have recognition molecules on their membranes called antigens. The immune system can usually tell the difference between its own body cells and “non-self” cells such as pathogens because of these antigens. Antigens on the surface of pathogens trigger a response from the immune system. White Blood Cells ♦ Some cells are specialized to surround and engulf pathogens. Other white blood cells produce antibodies (proteins that either attack the pathogens or mark them for killing). Antibodies “recognize” their antigen by matching molecule shape. Pathogens have antigens. Our bodies have antibodies against invader antigens. ♦ The marked invaders may then be engulfed by yet other white blood cells. ♦ Most white blood cells and antibodies disintegrate after defending the body, but some specialized white blood cells called memory cells remain. They are also known as B-cells. ♦ Memory cells are capable of quickly dividing and producing more antibodies of the same kind to fight off later invasions of the same microbes (microscopic organisms). Chunk! • What are recognition molecules on the surface of cells called? • What triggers an immune response? • What kind of cells engulf pathogens? • What are antibodies and how do they work? • What are memory cells? • Why don’t you get a sickness twice?