Homeostasis - Immune System
advertisement

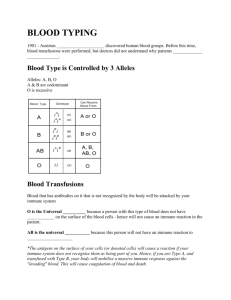
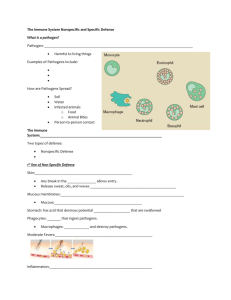
Aim: How are diseases related to homeostasis? Handout HW: Review book pg. 33-36 Q’s 54-69, pg. 41-42 Q’s31-34, 44 Castle learning: Immunity Disease is an abnormal condition of an organism that impairs bodily functions and can be deadly The failure of the homeostasis of an organism Qualified as contagious diseases (also called communicable diseases) can be transmitted from one person or species to another Qulaified as non-contagious diseases that may be caused by the environment and genetic disorders *contact with airborne droplets, spread by sneezing, coughing, talking, kissing or even singing *contact with bodily fluids, generally as a result of sexual activity *contaminated food and water *contact with a contaminated, inanimate object VECTORS: Any animal that can transmit a pathogen. Pathogen – any substance that can cause disease Examples –Mosquitos –Ticks –Raccoons Malaria, West Nile Virus Lyme Disease Rabies 1. Microorganisms invasion of pathogens (antigens) for example bacteria and viruses. 2. Harmful Lifestyle choosing activities that could leave your body vulnerable to infection. Examples – drugs, smoking, unsafe sex, malnutrition 3. Organ malfunction when an organ fails to properly function 4. Inheritance when there is a genetic predisposition to a disease 5. Pollution environmental pollution could include air pollution and water pollution. Examples are lead poisoning and asbestos poisoning Any substance that can cause the production of antibodies and prompt an immune response Found on the cell membrane of most pathogens EX. The outer covering of viruses. used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects, such as bacteria and viruses Microbes that enter the body, causing disease, are known as 1. 2. 3. 4. pathogens antibodies enzymes hosts IMMUNITY The ability of the body to fight infection through the production of antibodies or cells that inactivate foreign substances/invaders (pathogens) Any substance that can cause the production of antibodies and prompt an immune response Found on the cell membrane of most pathogens EX. The outer covering of viruses. video used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects, such as bacteria and viruses video The diagram below represents one possible immune response that can occur in the human body. The structures that are part of the immune system are represented by 1. A, only 2. A and C, only 3. B and C, only 4. A, B, and C Certain microbes, foreign tissues, and some cancerous cells can cause immune responses in the human body because all three contain 1. 2. 3. 4. antigens enzymes fats cytoplasm act as filters or traps for foreign particles and contain white blood cells functions in the destruction of extra red blood cells, and holds a reservoir of blood. stimulate the production of white blood cells Production of blood cells Lines of Defense First Line of Defense Physical barriers Skin acts as a barrier between the outside environment and the internal environment. Second Line of Defense Inflammatory Response Inflammation occurs when the physical barrier as been penetrated and the site of penetration becomes swollen and warmed. Third Line of Defense Immune Response When the immune system recognizes, attacks, destroys, and “remembers” pathogens. The immune response is carried out by the white blood cells. FINAL SUMMARY To replace burned skin, doctors can successfully transplant replacement skin taken from another part of the body of the burn victim. Which statement best explains why the transplanted skin is not rejected? 1. The transplanted skin is damaged, making the immune system nonfunctional. 2. The antigens of the replacement skin are the same as those of the damaged skin. 3. Burn victims lose so much blood that white blood cells cannot cause an immune response. 4. There is no blood supply to the skin, so mixing of antigens does not occur. The presence of parasites in an animal will usually result in 1. an increase in meiotic activity within structures of the host 2. the inability of the host to maintain homeostasis 3. the death of the host organism within twenty-four hours 4. an increase in genetic mutation rate in the host organism Which statement best describes an immune response? 1. It always produces antibiotics. 2. It usually involves the recognition and destruction of pathogens. 3. It stimulates asexual reproduction and resistance in pathogens. 4. It releases red blood cells that destroy parasites.