immune response - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
advertisement

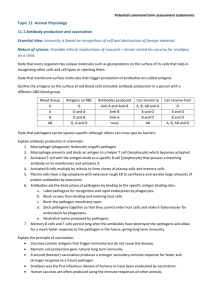
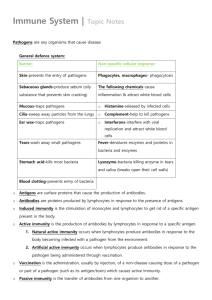
AIM: How does our body defends us from pathogens? DN: 1.Explain what a pathogen is. 2.Give two examples of types of pathogens and give a specific example for each type. 3.Will a Dr. give you antibiotics if you have a cold? Why or why not? HW: h/o tonsils DO NOW QUIZ 1. Explain what a pathogen is. 2. Give two examples of types of pathogens and give a specific example for each type. 3. Will a Dr. give you antibiotics if you have a cold? Why or why not? Pathogens Any disease-producing agent such as a virus, bacterium, fungus, or parasite. 1st Line of Defense • Skin –enzymes in sweat • Mucus–trap pathogens • Tears in eyes – enzymes to destroy pathogens • Acid in stomach- inhospitable to pathogens 2nd Line of Defense The Immune System White Blood cells • Large cells with a nucleus. • Less numerous than RBC’s. • Defenders of the body. • Types: – Phagocytes: engulf and destroy bacteria – Lymphocytes: produce antibodies Immune System Made of proteins, cells, and tissues that identify and defend the body against pathogens How does our immune system identify foreign cells? Antigen I.D. Tag • A protein on the cell • The ID tag identifies the invader as not belonging to the body (non-self). • This ID tag is called an antigen. Phagocytes Engulf the Pathogens Phagocytes: White blood Cells that Eat a pathogen Lymphocytes Produce antibodies • They can make antibodies, which are their weapons against the foreign antigens. • Antibodies & Antigens are both proteins!! Antibodies Pathogen Antibodies Antigens B Cells • They are “Y” shaped proteins, made Lymphocytes by __________ • They are weapons that fight against pathogens How are nuts and screws similar to antigens and antibodies? Antibodies are made specifically to match the shape of the antigen. 1 antigen = 1 antibody What does this remind you of? How do antibodies destroy pathogens? When the antibody attaches to the antigen, it breaks open its cell membrane • Or, the antibody attaches to the antigen, and a phagocyte will know to engulf it Our Immune System has a good memory! The first response is relatively slow and weak because time is needed for enough WBCs to form and defeat the pathogen. The second response to the same pathogen triggers a quicker and stronger response. ** After the first response, the immune system “remembers” specific pathogens by leaving behind WBCs that protect the body for years (memory cells).