Biology Chapter 5 Key Vocabulary Worksheet
advertisement

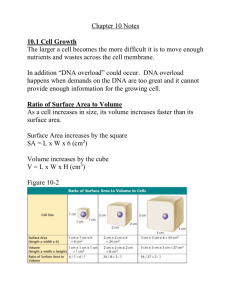
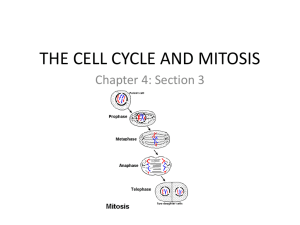
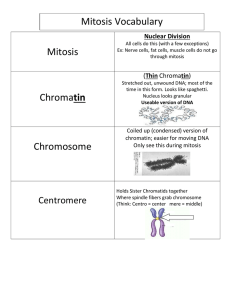
Name:__________________________________________ Biology Period___________ Date______________ Chapter 5 Key Vocabulary Review MATCHING Place the word and letter in the blank next to the correct definition. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. cell cycle mitosis cytokinesis chromosome histone chromatin chromatid centromere telomere prophase metaphase anaphase telophase Letter n. o. p. q. r. s. t. u. v. w. x. y. z. growth factor apoptosis cancer benign malignant carcinogen asexual reproduction binary fission tissue organ organ system cell differentiation stem cell Word Definition Groups of cells that work together to perform a similar function. Third phase of mitosis during which sister chromatids separate and are pulled to opposite sides of the cell. Broad group of proteins that stimulate cell division. Repeating nucleotide at the ends of DNA molecules that do not form genes and help prevent the loss of genes. Cell that can divide for long periods of time while remaining undifferentiated. Protein that organizes chromosomes around which DNA wraps. Common name for a class of diseases characterized by uncontrolled cell division. First stage of mitosis when chromatin condenses, the nuclear envelope breaks down, the nucleolus disappears, and the centrosomes and centrioles migrate to opposite sides of the cell. Group of different types of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or related functions. Region of condensed chromosome that looks pinched; where spindle fibers attach during mitosis and meiosis. Programmed cell death. Substance that produces or promotes the development of cancer. The asexual reproduction of a single-celled organism by division into two roughly equal parts. Last phase of mitosis when a complete set of identical chromosomes is positioned at each pole of the cell, the nuclear membranes start to form, the chromosomes begin to uncoil, and the spindle fibers disassemble. One half of a duplicated chromosome. Having no dangerous effect on health, especially referring to an abnormal growth of cells that are not cancerous. Two or more organs that work in a coordinated way to carry out similar functions. Process by which cell divides its nucleus and contents. Loose combination of DNA and proteins that is present during interphase. Process by which the cell cytoplasm divides. Second phase of mitosis when spindle fibers align the chromosomes along the cell equator. Pattern of growth, DNA replication, and cell division that occurs in a eukaryotic cell. Process by which unspecialized cells develop into their mature form and function. Cancerous tumor in which cells break away and spread to other parts of the body, causing harm to the organism’s health. Long, continuous thread of DNA that consists of numerous genes and regulatory information. Process by which offspring are produced from a single parent; does not involve the joining of gametes.