Unit 4B: Asexual Reproduction and Cell Division Test Study Guide
advertisement

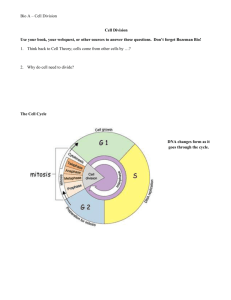
Name:________________________ Date:__________________ Unit 4B: Asexual Reproduction and Cell Division Test Study Guide Surface Area to Volume Ratio: Cells function best when… o The surface area of the cell membrane is __large______. o The volume of the cell is ___small_____. The best combination of surface area and volume factors is one in which (circle one) o the surface area is small / large o and the volume is small / large o the surface area to volume ratio: SA /V is small / large o Cells that conduct transport most efficiently will be (larger / smaller) cells Cell Division: Label the following structure: Be familiar with the “C” words involved in cell division: o Centromeres- area of DNA that joins two identical chromatids o Centrioles- small cylindrical structures made of microtubules that are found only in animal cells o Chromatid(s)- one arm of a double armed chromosome o Chromosomes- compact X shaped structures made of DNA o Chromatin-loosely packed DNA found in non-dividing cells Cell Cycle: What is binary fission? The prokaryotic cell cycle; a form of asexual reproduction o What organisms go through this process? Bacteria (Proks.) o On the box to the right, draw the process of binary fission. Interphase is an “in-between” period of _______growth_______ which consists of three phases. The M phase is where ___cell division__ actually occurs. This phases consist of o Mitosis or the _______division____ of the nucleus. o Cytokinesis or the ____division______ of the cytoplasm. What is the G0 phase? When does it happen? A period of rest that some cells go into right after the M phase. What is it? What happens during this phase of the cell cycle? (Bullet the important information!) (Write a short description) Interphase- in between period of growth G1- cells grow Grow in size make new proteins makes organelles S- DNA is synthesized (made) Chromatin is replicated By the end the cell will have double the DNA G2-preparing for cell division Cell makes proteins and organelles that are needed for division Now cell can divide! Prophase Metaphase M Phase- (Mitotic phase) parent cell divides into two daughter cells Mitosis- nucleus divides Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesiscytoplasm divides Longest phase of mitosis Chromatin condenses to from double armed chromosome (which attach at the centromere) Spindles begin to form- they extend from centrosome region (where centrioles are located) Centrioles travel to opposite ends of the cell or the poles By the end the nucleolus disappears The nuclear envelop breaks down. Shortest phase of mitosis Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell Spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of each chromosome (on both sides of the cell) Sister chromatids separate into single armed chromosomes and begin to move apart. Once each of them is at the opposite pole, anaphase is over. The condensed chromosomes relax into chromatin The spindle fibers break off Nuclear envelope begins to form around both clusters of chromosomes Nucleolus reforms in each daughter nuclei Mitosis is now complete Second part of the M phase Cytoplasm is split into half Cell splits into two Usually occurs at the same time as telophase Plant A cell plate is formed which becomes the cell wall. Animal A cleavage furrow is formed by the pitching of microfilaments. Draw the phase each cell is in and write a short description of what is happening at each phase. Regulating the Cell Cycle: What is apoptosis? When does it occur? Programed cell death that occurs when there is a problem with the cell that cannot be fixed Cancer is a ____disease___ of the cell cycle because it is ___uncontrolled_ cell division. A tumor is a ___mass________ of cells. o Malignant tumors ______invade___ and _destroy_ surrounding tissue. o Benign tumors do not ___spread__ to surrounding tissue. What causes cancer? Defects/mutations in genes that regulate the cell cycle. Only mutations in _sex_ cells (sperm and egg) will be passes from parent to offspring. Treatments for Cancer: Radiation Chemotherapy Surgery