Chapter 10 Notes
advertisement
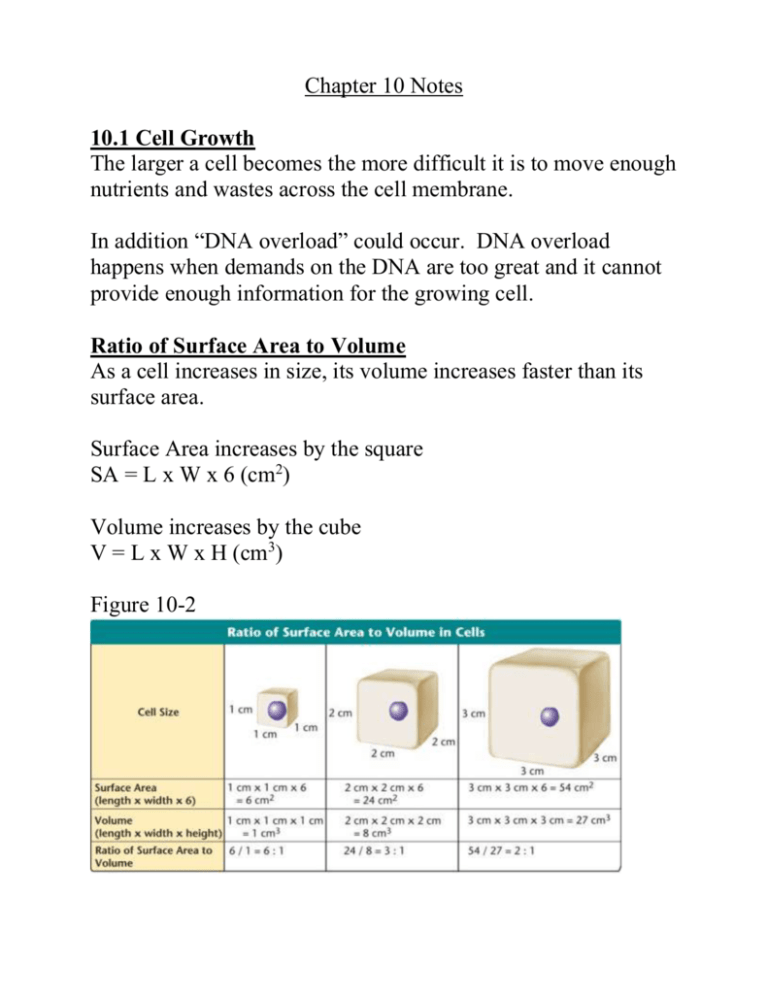
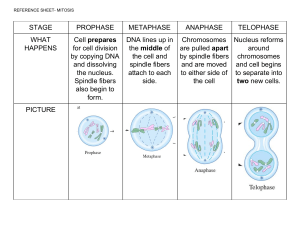
Chapter 10 Notes 10.1 Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes the more difficult it is to move enough nutrients and wastes across the cell membrane. In addition “DNA overload” could occur. DNA overload happens when demands on the DNA are too great and it cannot provide enough information for the growing cell. Ratio of Surface Area to Volume As a cell increases in size, its volume increases faster than its surface area. Surface Area increases by the square SA = L x W x 6 (cm2) Volume increases by the cube V = L x W x H (cm3) Figure 10-2 Division of the Cell Before a cell becomes too large, a growing cell divides forming two “daughter” cells. The process by which a cell divides into two new daughter cells is called cell division. 10-2 Cell Division Cell cycle is separated into three main parts. 1. Interphase 2. Mitosis (M Phase) 3. Cytokinesis Interphase – the period of growth that occurs between cell division. Interphase is composed of three parts – G1, S, G2 G1 – Growth phase #1, during this phase cells increase in size and synthesize new proteins and organelles. S - Synthesis, during this phase the chromosomes are replicated (DNA is synthesized). G2 - Growth phase #2, during this phase cells continue to replicate organelles and molecules required for nuclear division are produced. Cell division included Mitosis (M phase) and cytokinesis. Mitosis (M phase) is division of the cell nucleus and is broken down into 4 main phases and can last from a couple of minutes to several days. 1. Prophase 2. Metaphase 3. Anaphase 4. Telophase Prophase - (longest phase of mitosis) Chromosomes condense and become visible Nuclear membrane breaks down Nucleolus disappears Centrioles migrate to opposite poles Spindle fibers begin to form Metaphase - Chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. Each chromosome is connected to a spindle fiber at its centromere. Anaphase - Spindle fibers separate sister chromatids and move them to opposite sides of the cell. Telophase - Chromosome begin to unwind. Two new nuclear membranes begin to form. Spindle fibers begin to break up. Cytokinesis - division of the cytoplasm Takes place at the same time as telophase Figure 10-4 Cell Cycle Chromatids - one of two identical “sister” parts of a duplicated chromosome. Centrioles - help form spindle fibers during cell division. Spindle - made of microtubules and help move and separate the chromosomes during cell division. 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Proteins called cyclins regulate the cell cycle. Internal regulators allow the cell to proceed only when certain processes have happened inside the cell. External regulators such as growth factors will cause the cell cycle to speed up or slow down and responds to external stimuli. Cancer is a disorder in which some of the body’s own cells lose the ability to control growth. Cancer cells do not respond to the signals that regulate the growth of cells. Tumor = mass of uncontrollably dividing cells. When a tumor stays in place it is called benign. When some tumor cells break off and travel to different parts of the body they are called malignant.