MITOSIS
advertisement

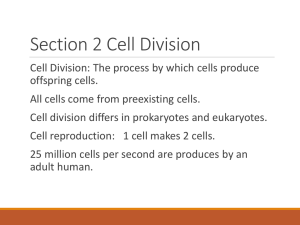
THE CELL CYCLE AND MITOSIS Chapter 4: Section 3 Little review here • Why does it matter that cells can transport materials across their cell membranes? • Why are photosynthesis and cellular respiration important to cells? Thinking ahead • Why do cells need to divide? • 1 • 2 • 3 A few things you need to know first: • Your DNA, actually everything’s DNA, even a blueberry’s, is divided into lengths called __________________________ • Different species have different numbers of chromosomes • The DNA that controls a certain trait, like height, is called a ______________ • There are many genes on each chromosome A few things you need to know first: • Why do we care about DNA, genes and chromosomes? • In eukaryotes like us, we have 2 genes for each trait –one from mom and one from dad • These genes are on similar chromosomes—1 from mom and 1 from dad--- called homologous (homo= __________, log = ______________) chromosomes The Cell Cycle How does dividing fit into the cell’s life? • Cell cycle = stages of the cells life • A cell’s cycle (life) starts when it is formed (by dividing) and ends when it divides again What happens in between? (Interphase) • Cells do their jobs How do cells divide? • Have to make enough organelles for 2 cells • Have to make enough DNA for 2 cells • Have to separate and divide organelles, cytoplasm, and DNA into 2 cells • http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/ch apter2/animation__how_the_cell_cycle_work s.html Interphase • Also known as the ________________ stage • Cell is involved in growth and ________________ activities: what does that mean? Interphase can be broken down into 3 sub-phases G1- S- G2- Mitosis = nuclear division 4 stages • Prophase (pro means ____________) • Metaphase (meta means _______________) • Anaphase • Telophase (telo means____________) Prophase • DNA condenses (and becomes visible) • Why is this important? Prophase • The 2 copies of each chromosome are called ____________________________ • They are held together at the ______________ • The _____________________ breaks down • Spindle fibers (protein strands that can get longer or shorter) form • ___________ move to opposite ends of the cell Metaphase • The double-stranded chromatids (this means the 2 copies of the same chromosome line up at the ___________________ _ of the cell • The spindle fibers attach to each chromatid (and to the centriole- that will help them pull apart the chromatids) Anaphase • The sister chromatids _______________ ___________________ • (hint for remembering: Away and Anaphase both start with A) • Spindle fibers contract and pull apart chromatids, centrioles help Telophase • The chromosomes reach opposite sides of the cell • The nuclear envelope (nuclear membrane) starts to __________________ • Spindle Fibers disappear • The chromosomes start to ________________ Mitosis is now finished • Do you have 2 cells now? • Cytokinesis: • http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::535::535::/sit es/dl/free/0072437316/120073/bio14.swf::Mitosis%20 and%20Cytokinesis Why is it important for: • The DNA to divide equally? • DNA to be coiled during mitosis? • DNA to uncoil during interphase? Some extra stuff: prokaryotic cells • Prokaryotic cells divide by _____________________ ______________ • Easy because they only have _________ chromosome • Easy because they do not have any _____________________ _____________________ Some extra stuff: plant and fungi cells • What about the cell walls? • During cytokinesis: a cell plate forms and becomes the new cell membranes • Then, the new cell wall forms between the cell membranes When mitosis goes wrong • Cell gets old and slow at mitosis? • Cell goes through mitosis and cell division way too much? • http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/cancer/grows.html