What molecules make up living things
advertisement

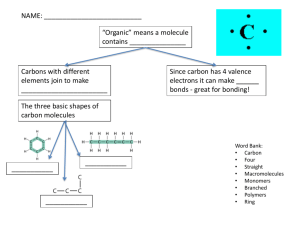
What molecules make up living things? Two Types of Molecules That Make Up Living Things ORGANIC • Must contain the element carbon • Found in living organisms • Some organic molecules contain hydrogen and oxygen • Some contain nitrogen Ex: Carbs, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids INORGANIC • Any molecule that is not organic is inorganic • Does not contain carbon – Exception is CO2 doesn’t contain H – Ex: Water LIVING THINGS MUST CONTAIN BOTH Where do we find these organic macromolecules? • In living organism’s cells • In the foods that we eat Food Label Analysis- With your partner, look at this food label and discuss the following… • Identify the organic macromolecules that have been discussed so far • Which macromolecule is has the highest value? Lowest? • What are some of the biological functions of this food based on the macromolecules that make it up? • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s16Tfrw 114&feature=related 4 Kinds of Organic Compounds • • • • Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids THESE MOLCULES CAN ALSO BE CALLED MACROMOLECULES MACRO= BIG MOLECULES= DIFFERENT ELEMENTS How do carbohydrates look? • Ring shaped • Contains C,H,O • C6H12O6 is the main carbohydrate called GLUCOSE 1:2:1 Ratio Carbohydrate Scientific Name • Monosaccharide is the monomer (building block) name Mono=one monosaccharide(single carb) glucose • Monosaccharides can join together to form… Di= two disaccharide (double sugar) glucose+ glucose= maltose glucose +fructose= sucrose glucose+ galactose= lactose Poly more than two (polysaccharide) Examples of Carbohydrates • Monosaccharides – Glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose • Dissacharides – sucrose, lactose, maltose • Polysaccharides – Starch, cellulose, chitin, glycogen Disaccharides Polysaccharides Carbohydrates- Biological Function and Features • Main source of usable energy for organisms • Used in the presence of oxygen to generate cellular energy (ATP) • Carbohydrates make up part of our cell membrane (hydrophobic) • Sweet in flavor – Starch is an important complex carbohydrate (polysaccharide) made from glucose – Cellulose is a polysaccharide carbohydrate that make up plant cell walls raw veggies are crunchy because you are eating the cell wall. WE CALL IT FIBER!!! – We store carbohydrates in the liver in a form called GLYCOGEN (polysaccharide) Carbohydrate Chain on Outside of cell membrane How do living things obtain these carbohydrates? • Food that they eat – Grains and plants How are these molecules made and biochemically stored in organisms? Dehydration Synthesis (Condensation) How does condensation occur? • One molecule of water is lost for every monosaccharide molecules that come together. • Two molecules are then covalently bonded. • Can continue to form long chains called polymers How do organisms break large carbohydrates for usage? • Hydrolysis • Using water to split di- and polysaccharides in order to form monosaccharides (glucose) • The monosaccharides can then be used by cell to generate cell energy (ATP) Hydrolysis Animation • http://nhscience.lonestar.edu/biol/dehydrat /dehydrat.html • http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/conte nt/chp03/0302002.html Lipids • Also known as fats or oil – Fat: solid at room temperature – Oil: liquid at room temp Monomer building blocks of two parts: Glycerol and 3 fatty acids Forming a lipid molecule 3 fatty acids molecules 1 glycerol Process used to form a lipid molecule • Condensation (Dehydration Synthesis) • 3 Water molecules are drawn out to form one lipid molecule • Forms a triglyceride molecule Lipid formation animation and information • http://nutrition.jbpub.com/resources/animat ions.cfm?id=10&debug=0 • http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/conte nt/chp03/0302002.html One Lipid molecule SHAPED LIKE A LETTER E Biological Function • Lipids chiefly function in energy storage, protection, and insulation in living things • A main component of cell membranes – Fats: found in animals – Oils: found in animals and plants. Waxes: found in plants solid at room temp. – Steroids: contain fat compounds ( biological hormones, cholesterol) Ways to Recognize a Lipid • 3 Fatty acid chains • Shaped like a letter E • Large and long molecule Types of lipids (fats) • Unsaturated lipid (fats): – the fatty acid component contains C bonded to C using a double bond or a triple bond Types of lipids (fats) • Polyunsaturated Lipids These lipids have more than one double or triple bond in their fatty acid tails • Saturated lipids (fats): all carbon in the fatty acid chains are single bonded What is a protein? • Proteins are organic molecules that play an important role in • • • • Growth and repair of cells Can be used for energy Helps to keep a stable body temperature Growth and repair and support of muscle tissue, hair, skin, nails (ex. Keratin and collagen) • Carry out genetic instruction from the nucleus • Helps to speed up biochemical reactions • Fighting off infections (antibodies) Composition of Proteins • Monomer: Amino Acid • 3 Parts to an amino acid: Amino Group, R side chain, carboxylic acid group How do amino acids come together? • Dehydration synthesis (condensation) • Results in a PEPTIDE BOND How do amino acids come together How do amino acids form proteins? Condensation/ Dehydration Synthesis • Forms a peptide bond when amino acids combine • 2 a.a. coming together= DIPEPTIDE • 3 or more a.a. coming together = POLYPEPTIDE • 50-3000 a.a. linked together considered a PROTEIN Animation- Protein • http://nhscience.lonestar.edu/biol/dehydrat /dehydrat.html • http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/conte nt/chp03/0302002.html How can proteins change? • http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/a nimations/content/proteinstructure.html What are nucleic acids? • Compounds that contain phosphorus and nitrogen in addition to other organic elements C,O,H • Found in hereditary material in the form of DNA or RNA Monomer for Nucleic Acids • Arranged as repeating NUCLEOTIDES • Three parts to the nucleotide – Phosphate backbone – Sugar molecule – Nitrogenous base DNA- Deoxyribonucleic Acid • Contains the genetic hereditary code that makes each of us different. Our genetic “blueprint” What is RNA? • RNA= ribonucleic acid • RNA is single stranded • Controls genetic messages of the cell to form proteins for the cell. RNA Picture • http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/conte nt/chp03/0302002.html • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H8WJ2 KENlK0 (