Core Concepts of
ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Moscove, Simkin & Bagranoff
Developed by:
S. Bhattacharya, Ph.D.
Florida Atlantic University
John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Chapter 8
Accounting and Enterprise Software
• Introduction
• Integrated Accounting Software Programs
• Enterprise-Wide Accounting Software
Solutions
Integrated Accounting
Software Programs
• Most companies purchase accounting and enterprise
software.
• Another option is to “e-source” the software by
buying the services of an application service provider
(ASP).
• Integrated accounting software programs process all
types of accounting transactions.
• Packages today include Internet connectivity and
enable small businesses to create Web sites and
engage in electronic commerce.
• Middle to high-end accounting software packages are
typically sold by a value-added reseller (VAR).
Enterprise-wide Accounting
Software Solutions
• Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems are
integrated programs do much more than process
financial data.
• The capabilities of accounting software programs
to process enterprise-wide data expand with the
price and complexity of software.
• A valued feature of ERPs is the ability to interface
with customers and suppliers. This is termed
supply chain management.
Specialized Accounting
Software
• Accounting software has become more
sophisticated and customized for specific industry
information needs.
• Specialized accounting software may include:
– Customer relationship management to keep
track of sales calls, seminars, and phone calls
with prospective clients
– Source code that may be customized
to fit a particular firm’s needs.
Enterprise-Wide Accounting
Software Solutions
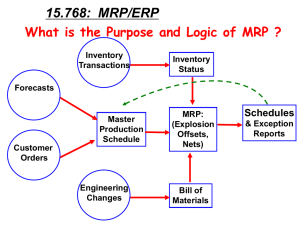
• Enterprise System Functionality: ERP systems
originated from manufacturing systems
– MRP I Systems: Marketing sales projections,
Production schedules
– MRP II Systems: MRP I plus Forecasting and
planning for all manufacturing resources including
labor and overhead
• ERP Systems combined MRP II systems with
accounting and finance functions
Traditional ERP Functions
•
•
•
•
Order processing and fulfillment
Manufacturing
Purchasing
Human resources
Extended ERP Systems
• Traditional back-office capabilities of
traditional ERP systems, plus…
–
–
–
–
–
E-business
Customer management
Supplier management
Business partner management
Strategic business relationship management
The Architecture of Enterprise
Systems
• ERP Configurations
• Centralized database
• Application interfaces
– Extended application interfaces
• Internet portals
Business Processes and
Enterprise Systems
• Integrated Business Processes
• ERP Systems and Business Process
Reengineering
Implementing an Enterprise
System
• Systems Planning and Forming the Project
Team
• Software and Consultant Selection
• Preimplementation Work
• Go Live and Follow-up
• Training and Change Management
Costs and Benefits of
Enterprise Systems
Costs
• Hardware
• Software
• Training
– Technical
– Business processes
•
•
•
•
•
•
Data conversion
Interfaces and customization
Professional services
Reassigned employees
Software maintenance
Software upgrades
Benefits
•
•
•
•
Reduced inventory investment
Improved asset management
Improved decision-making
Resolved data redundancy and
integrity problems
• Increased flexibility and
responsiveness
• Improved customer service and
satisfaction
• Global and supply chain
integration
Copyright
Copyright 2005 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in
Section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without the
express written permission of the copyright owner is unlawful.
Request for further information should be addressed to the
Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. The purchaser may
make backup copies for his/her own use only and not for distribution
or resale. The Publisher assumes no responsibility for errors,
omissions, or damages, caused by the use of these programs or from
the use of the information contained herein.
Chapter 8