Chapter 8 Integrated Accounting Software Programs Types of
advertisement

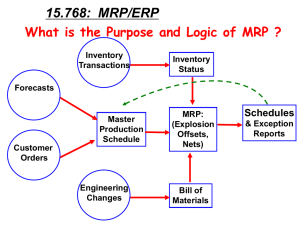
Core Concepts of ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEMS Moscove, Simkin & Bagranoff Developed by: S. Bhattacharya, Ph.D. Florida Atlantic University Chapter 8 Accounting and Enterprise Software • Introduction • Integrated Accounting Software Programs • Enterprise-Wide Accounting Software Solutions John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Integrated Accounting Software Programs • Most companies purchase accounting and enterprise software. • Another option is to “e-source” the software by buying the services of an application service provider (ASP). • Integrated accounting software programs – process all types of accounting transactions. – G/L, Sales, Purchasing, Payroll, Job Cost, etc. • Packages today include Internet connectivity and enable small businesses to create Web sites and engage in electronic commerce. • Middle to high-end accounting software packages are typically sold by a value-added reseller (VAR). Types of Accounting Software • Small – Medium ($100 mm - $500 mm, 100 – 500 employees) – Business software ($3,000 - $100,000 cost) • • • • Microsoft (Great Plains, Solomon) MAS 90 ACCPAC Macola – Enterprise ($20,000 - $500,000 cost) • Microsoft, MAS, ACCPAC & more Types of Accounting Software • Entry Level – Smaller business (up to $5mm revenue, 20 employees) – Cost $100 - $4,500 – Examples • Peachtree • Quickbooks Types of Accounting Software • Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) – > $500 mm revenue, > 500 employees – $400,000 - $300,000,000 cost • • • • SAP PeopleSoft Oracle BAAN • Industry specific • Custom Built Enterprise-wide Accounting Software Solutions • Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems – integrated programs – do much more than process financial data. • Capabilities to process enterprise-wide data expand with the price and complexity of software. • A valued feature of ERPs – the ability to interface with customers and suppliers. – This is termed supply chain management. Specialized Accounting Software • Accounting software has become more sophisticated and customized for specific industry information needs. • Specialized accounting software may include: – Customer relationship management to keep track of sales calls, seminars, and phone calls with prospective clients – Source code that may be customized to fit a particular firm’s needs. Enterprise-Wide Accounting Software Solutions • Enterprise System Functionality: ERP systems originated from manufacturing systems – MRP I Systems: Marketing sales projections, Production schedules – MRP II Systems: MRP I plus Forecasting and Traditional ERP Functions • • • • Order processing and fulfillment Manufacturing Purchasing Human resources planning for all manufacturing resources including labor and overhead • ERP Systems combined MRP II systems with accounting and finance functions Extended ERP Systems • Traditional back-office capabilities of traditional ERP systems, plus… – – – – – E-business Customer management Supplier management Business partner management Strategic business relationship management • See graphic on pg 251 The Architecture of Enterprise Systems • ERP Configurations • Centralized database • Application interfaces – Extended application interfaces • Internet portals Business Processes and Enterprise Systems • Integrated Business Processes – Not just within company – Also between companies • ERP Systems and Business Process Reengineering – Do make it work, better be ready to function efficiently using best practices. – But don’t lose sight of what makes you unique! Implementing an Enterprise System • Systems Planning and Forming the Project Team • Software and Consultant Selection • Pre-implementation Work • Go Live and Follow-up • Training and Change Management Costs and Benefits of Enterprise Systems Things to consider Costs • Time to implement – Training (learning and re-learning) – Data conversion • Resistance to change • Business cycle • Support costs – Platforms (Unix, Linux, Microsoft) – Mergers of providers • How to measure the benefit Assignment • Pick a unique industry • Research types of accounting software available (plural – so at least 2) • Find 3 VAR’s • Bring to class and be ready to discuss what is unique about the software • • • Hardware Software Training – Technical – Business processes • • • • • • Data conversion Interfaces and customization Professional services Reassigned employees Software maintenance Software upgrades Benefits • • • • • • • Reduced inventory investment Improved asset management Improved decision-making Resolved data redundancy and integrity problems Increased flexibility and responsiveness Improved customer service and satisfaction Global and supply chain integration