INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
advertisement

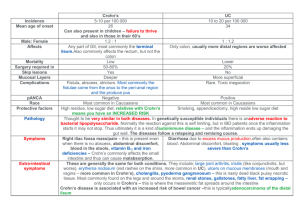
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Anusha Reddy FY1 SWFT 3rd Feb 2014 OBJECTIVES 2 Case Studies: Crohn’s Vs Colitis THINK: AETIOLOGY EPIDEMIOLOGY SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS INVESTIGATIONS MANAGEMENT CASE STUDY 1 22 Female PC: 6/52 of 5 x loose, non-bloody stools daily Right lower quadrant abdominal pain (especially after eating) 8kg weight loss Bilateral knee and ankle pains MORE INFORMATION REQUIRED Full history Nil PMH, no hx of foreign travel No medications or allergies Current smoker- 5 pack-years Examination Definite and moderately tender 5-cm mass in the right lower quadrant No joint effusion or skin lesions are noted DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Gastroenteritis Crohn’s Disease Ulcerative Colitis Irritable Bowel Syndrome Behcet’s Disease Bowel Cancer Tuberculosis Amyloidosis Acute Appendicitis WHAT DO WE THINK THIS IS? 22 Female PC: 6/52 of 5 x loose, non-bloody stools daily Right lower quadrant abdominal pain (especially after eating) 8kg weight loss Bilateral knee and ankle pains CROHN’S DISEASE- DEFINITION Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Unknown Aetiology Characterised by 1. 2. 3. 4. Focal Asymmetrical Transmural Occasionally granulomatous inflammation Any part of the GI tract- mouth anus CROHN’S DISEASE- EPIDEMIOLOGY Incidence: 9.56 per 100,0001 Prevalence: 115,000 in the UK Age of onset: 2 peaks 1) 15-30 Y (more common) 2) 60-80 Y Female: Male 1.8:1 Children this is reversed! Risk Factors2 Mycobacterium paratuberculosis, Pseudomonas spp. & Listeria spp. ↑TNF-alpha High-fat diets Genetic mutations 1) Steed H, Walsh S, Reynolds N; Crohn's disease incidence in NHS Tayside. Scott Med J. 2010 Aug;55(3):22-5 2) Rangasamy P et al; Crohn Disease, Medscape, Jun 2011 CROHN’S DISEASE- SYMPTOMS • • • • • • • • • • Abdominal pain, cramping or swelling Anaemia Fever Gastrointestinal bleeding Joint pain Malabsorption Persistent or recurrent diarrhoea Stomach ulcers Vomiting Weight loss CROHN’S DISEASE- ON EXAMINATION General ill health- weight loss & dehydrated Hypotension, tachycardia and pyrexia Abdominal tenderness or distension, palpable masses. Anal and perianal lesions (abscesses, fistulae) Mouth Ulcers Extra-intestinal manifestations of Crohn’s ...... CROHN’S DISEASE- EXTRA INTESTINAL INVESTIGATIONS Bloods FBC, CRP, U&Es, LFTs Stool culture and microscopy anti-S. cerevisiae antibodies Perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (p-ANCA) (UC>CD) Abdo Xray Ileocolonscopy and biopsy from the terminal ileum as well as the affected sites Small bowel follow through If upper GI symptoms- Upper GI endoscopy If lower GI symptoms- Flexible sigmoidoscopy/EUA CROHN’S DISEASE- MANAGEMENT 1. First presentation (NICE guidelines) Glucocorticoids 1. 2. 3. Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone IV hydrocortisone Budesonide 5-ASA +/- ADD ON Azathioprine or Mercaptopurine Biologic: Infliximab and Adalimumab CROHN’S DISEASE- MANAGEMENT Maintaining Remission (NICE guidelines) Offer Azathioprine or Mercaptopurine as Monotherapy Methotrixate Surgery- if limited to distal ileum (weighing out the risk Vs benefits) and for complications... CROHN’S DISEASE- COMPLICATIONS B A C C CASE STUDY 2 32 Male Bloody diarrhoea 4/52 Bilateral lower abdominal cramping Malaise and weight loss No associated fever, visual changes, arthralgias, or skin lesions Previously fit and well contractor Non-smoker, 14-18 units/week drinker FHx: Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 ULCERATIVE COLITIS- DEFINITION Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Disease Unknown aetiology Only Large Colon Classification: Distal Disease More extensive disease Pancolitis ULCERATIVE COLITIS- EPIDEMIOLOGY More common than Crohn’s Incidence: 10 per 100,000 Prevalence 240 per 100,000 in the UK Age of onset: 2 peaks 1) 15-25 Y (more common) 2) 55-65 Y Male:Female= 1:1 Idiopathic: ?autoimmune condition triggered by colonic bacteria inflammation Genetic component: sibling of an individual who has IBD 17-35 x more risk of development Risk of UC decreased in smokers 1) Ulcerative Colitis; NICE Clinical Guideline (Jun 2013) ULCERATIVE COLITIS- SYMPTOMS Bloody diarrhoea Abdominal Pain Tenesmus Systemic symptoms: malaise, fever, weightless ULCERATIVE COLITIS- ON EXAMINATION Unwell, pale, febrile, dehydrated Abdo pain and tenderness .. + distension TOXIC MEGACOLON Worrying signs: Tachycardia, anaemia and fever Extra- intestinal disease... ULCERATIVE COLITIS- EXTRA-INTESTINAL Aphthous ulcers Ocular manifestations 5% Episcleritis Anterior uveitis Acute arthropathy affecting the large joints 26% Sacroiliitis Ankylosing Spondylitis 3% Deramatology 19% Pyoderma gangrenosum Erythema nodosum Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis ULCERATIVE COLITIS- INVESTIGATIONS Bloods: FBC, LFTs, U+Es, CRP Serology- pANCA Vs. ASCA Stool cultures Imaging Abdo x-ray- acute setting Barium enema- can show mucosal structure Flexible Sigmoidoscopy and Biopsy- for diagnosis ULCERATIVE COLITIS- MANAGEMENT a) Topical aminosalicylate alone (suppository or enema b) ?ADD PO aminosalicylate to a topical aminosalicylate OR c) consider an PO aminosalicylate alone a) PO Aminosalicylate - High induction dose of an b) ?ADD topical Aminosalicylate OR PO beclometasone dipropionate - If no improvement 72 hrs despite IV Hydrocortisone OR -Symptoms worsen to pancolitis: a) ADD IV Ciclosporin to IV steroids ULCERATIVE COLITIS- MANAGEMENT Indications for Surgery: Unresponsive to medical treatment Significantly affecting quality of life Growth retardation in Children Life-threatening complications... Bleeding Toxic Megacolon Impending perforation Carcinoma ANY QUESTIONS? SUMMARY SUMMARY: CROHN’S VS. UC (1) Symptoms of Crohn's Disease Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis • Abdominal pain, cramping or •Bloody diarrhoea swelling •Abdominal pain or discomfort •Anaemia •Anaemia caused by severe •Fever bleeding •Gastrointestinal bleeding •Dehydration •Joint pain •Fatigue •Malabsorption •Fever •Persistent or recurrent •Joint pain diarrhoea •Loss of appetite •Stomach ulcers •Malabsorption •Vomiting •Rectal bleeding •Weight loss •Urgent bowel movements •Weight loss SUMMARY: CROHN’S VS. UC (2) SUMMARY- CROHN’S VS. UC (3) SUMMARY: CROHN’S VS. UC (2) LEARNING POINTS RELAPSE AND REMITTING MANAGE THE PATIENT BONE PROTECTION- IF ON LONG-TERM STROIDS TEST FOR TB BEFORE STARTING INFLIXIMAB RISK OF COLONIC CARCINIMA IN UC THANK YOU!!