plant structure
advertisement
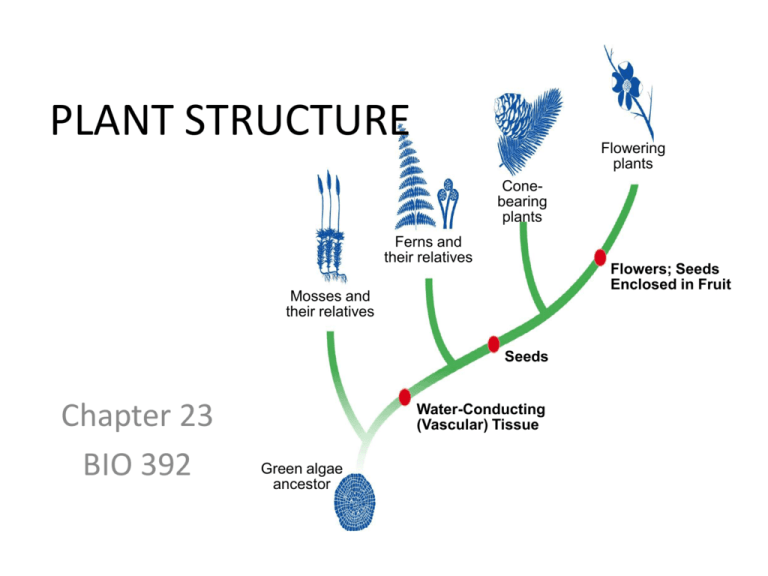
PLANT STRUCTURE Flowering plants Conebearing plants Ferns and their relatives Flowers; Seeds Enclosed in Fruit Mosses and their relatives Seeds Chapter 23 BIO 392 Water-Conducting (Vascular) Tissue Green algae ancestor Remember… • Organisms are made up of: – Organ Systems – Organs – Tissues – Cells • • • • Plants are made up of: Organ Systems Organs: Roots, Stems, Leaves Tissues: Dermal, Vascular, Ground, Meristematic • Cells: epidermal cells, tracheids, vessel elements, sieve tube elements, companion cells, parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma, Concept Map Section 23-1 Plant Tissues include Dermal tissue Meristematic tissue includes Epidermal cells includes Xylem includes Tracheids Vascular tissue Vessel elements Ground tissue includes Phloem Parenchyma cells includes Sieve tube elements Companion cells Collenchyma cells Schlerenchyma cells PLANT TISSUE SYSTEMS (4) A) MERISTEMATIC Source of new growth for the entire life of the plant • Primary Growth plants grow taller and deeper – Only in tips of roots & shoots – Apical meristem “the bud” • Secondary Growth plants grow wider – Lateral Meristem tissue – (Also known as: vascular or cork cambium) PLANT TISSUES cont. B) DERMAL TISSUE The outer covering of the plant, “the skin” – May have waxy covering to prevent water loss C) VASCULAR TISSUE transports fluids & nutrients throughout the plant, “the bloodstream” – Xylem transports water – Phloem transports food (sugars made) D) GROUND TISSUE everything else 3 Plant Organs • Roots • Stems • Leaves ROOTS FUNCTION 1. Absorbs water & dissolved nutrients from soil 2. Anchors plant & prevents erosion TYPES: 1. Taproots long & thick, 2. Fibrous roots thin & branching ROOTS cont. STRUCTURE (by tissue) & TRANSPORT 1. Outer epidermal layer a. covered by tiny root hairs – more S.A. b. contain active transport proteins in their cell membranes to pump minerals from soil into plant. c. water follows by osmosis ROOT STRUCTURE cont. 2. Large layer of Ground tissue a. spongy cortex b. endodermis encloses vascular tissue i. cells are surrounded by Casparian strips - waterproof barriers that force water to go through cells, not around. - Keep flow one way (osmosis) 3. Central Vascular cylinder a. water moves into the xylem b. because it cannot go backward, the only place to go is up the stem i. “Root Pressure” STEMS FUNCTION 1. Support; hold leaves up in the sunlight 2. Transport substances between roots & leaves TRANSPORT 1. Capillary Action a. water moves by cohesion from roots b. 1 way 2. Nutrients are transported through stem a. in phloem b. in 2 directions LEAVES FUNCTION 1. Site of Photosynthesis STRUCTURE 1. epidermis is covered by cuticle a. reduce evaporation 2. Mesophyll – specialized ground tissue a. lots of chloroplasts b. where photosynthesis occurs 3. Veins of xylem & phloem branch LEAVES cont. SPECIAL STRUCTURES 1. Stomata exterior openings on underside of leaf. Site of gas exchange (pores) a. O2 out b. CO2 in c. water vapor out 2. Guard cells surround and control stomata openings LEAVES cont. TRANSPORT 1. Water escapes through stomata a. process of transpiration (evaporation) b. as water exits, more is drawn up through stem from roots 2. Stomata open and close to prevent excessive water loss. Shoots and Roots Stem











