SBI 3U Exam Review Unit #5 - Plants: Anatomy and Functions
advertisement

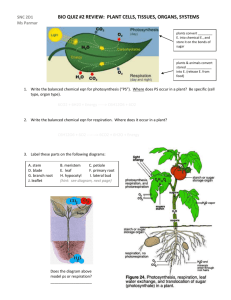
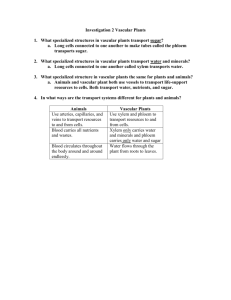
SBI 3U Exam Review Unit #5 - Plants: Anatomy and Functions *Study any diagrams included in your notes from this unit Review Questions: 1. Distinguish between monocot and dicot plants using 4 different characteristics. 2. How do vessel cells differ from tracheids? 3. What is the relationship between sieve tube cells and companion cells? 4. What are some differences and similarities between xylem and phloem 5. What is the major role of xylem? of phloem? 6. How does the transpiration-cohesion (tension) theory explain how water is able to reach to the tips of tall trees? 7. What are some factors regarding how phloem accomplishes translocation of sugars in the plant? 8. What is the major role of the leaf? 9. Describe epidermis cells and explain what function they have. 10. What substance does the epidermis secrete and what is its function? 11. What are the characteristics of the two guard cells that comprise a stoma? 12. How does the stoma open and close? 13. Under what conditions would the stomata likely be closed? Why? 14. When would the stomata likely be open? 15. Why is their a need for air spaces in the spongy mesophyll? 16. What is the primary function of spongy mesophyll cells and palisade cells? 17. Describe a rhizome. 18. What is the function of pith and cortex cells in the stem? 19. What are the major roles of roots? 20. Describe the differences between tap roots and fibrous roots. What advantage does each type have? 21. Name the four major regions of a growing root tip and describe briefly what occurs in each region. 22. What are root hairs, and what is their function? 23. What is the role of the endodermis of the root? 24. What is the vascular cylinder in the root? 25. Describe meristem tissue and its role. 26. Describe the development of wood tissues in a dicot with vascular cambium cells using a series of diagrams. Label: spring xylem, summer xylem, pith, vascular bundle, phloem, annual ring. 27. What is a hormone? 28. Explain the role of auxins in plants. 29. Give an example of and explain a tropism? Vocabulary: vascular plant seed leaves cotyledon monocot dicot seed herbaceous stem woody xylem phloem tracheids vessel cells sieve tube cell companion cell root pressure capillary action cohesion-tension theory translocation in phloem vascular bundles epidermis cuticle stomate guard cell spongy mesophyll palisade mesophyll vein in leaf stem rhizome tuber vascular cambium growth ring (annual ring) meristem pith spring xylem summer xylem roots fibrous roots tap root endodermis vascular cylinder cortex root hairs zone of maturation zone of elongation hormone auxin abscisic acid tropism stimulus phototropism hydrotropism gravitropism artificial selection pure line selection crossbreeding monoculture crop rotation