Chapter 6: General Anatomy, and Physiology
advertisement

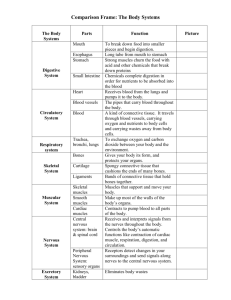
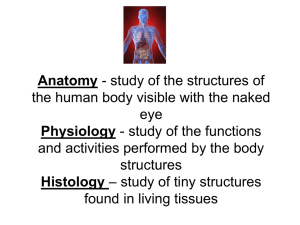
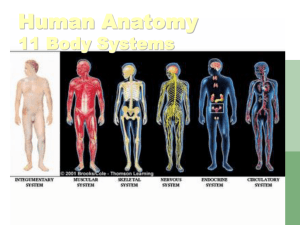
2014 Level 2 Final Exam Review – 12’ – Part III Page 1 of 7 Chapter 6: General Anatomy, and Physiology I. II. A. B. C. D. Anatomy, Physiology, and You A. Anatomy – Study of human body structures that can be seen with the naked eye and how the body parts are organized B. Physiology – study of the functions and activities performed by the body’s structures C. –Ology – means study of D. Histology – study of tiny structures found in living tissue Cells Basic unit of all living things Parts 1. Protoplasm – colorless, jellylike substance in which food elements are present 2. Nucleus – found in the center and plays an important part in reproduction of the cell 3. Nucleolus – small spherical body, composed of RNA and protein, within the cell nucleus 4. Cytoplasm – found outside the nucleus and contains food materials necessary for growth, reproduction and self repair of the cell 5. Centrosome – small round body in the cytoplasm, which affects the reproduction of the cell 6. Cell Membrane – encloses the protoplasm, permits soluble substances to enter and leave the cell Cell Growth 1. Adequate supply a. Food b. Oxygen c. Water d. Eliminates waste products e. Favors with proper temperature 2. Mitosis – cell division Cell metabolism 1. Complex chemical process whereby the body cells are nourished and supplied with the energy needed to carry on their many activities 2. Anabolism – the process of building up larger molecules from smaller ones 3. Catabolism – the breaking down of larger substances or molecules into smaller ones to release energy 4. Homeostasis – the maintenance of normal internal stability in the Organism Page 2 of 7 5. II. III. IV. V. Fat – molecules of energy not used turn into Tissues A. Connective tissue – serves to support, protect and bind together other tissues of the body. B. Muscular tissue – contracts and moves various parts of the body C. Nerve tissue – carries messages to and from the brain, and controls and coordinates all body functions D. Epithelial tissue – is a protective covering on body surfaces E. Liquid tissue – carries food, waste products and hormones by means of the blood and lymph Organs A. Structures designed to accomplish a specific function B. Brain – controls the body C. Heart – circulates the blood D. Lungs – supply oxygen to the blood E. Liver – removes toxins products of digestion F. Kidneys – excrete water and other waste products G. Stomach and Intestines – digest food Systems A. Groups of organs that cooperate for a common purpose B. Integumentary system – skin C. Skeletal system – bones D. Muscular system – muscles E. Nervous system - nerves F. Circulatory system – blood supply G. Endocrine system – ductless glands H. Excretory system – organs of elimination I. Respiratory system – lungs J. Digestive system – stomach and intestines K. Reproductive system – organs for reproducing Skeletal system A. Physical foundation of the body B. Bone – second hardest tissue of the body C. Tooth – hardest tissue of the body D. Osteology – scientific study of bones, their structure and functions E. Functions 1. Give shape and support 2. Protect various internal structures and organs 3. Serve as attachments and act as levers to produce body movements 4. Produce blood cells in the red bone marrow 5. Store various minerals F. 8 Bones of the skull 1. Occipital 2. Parietal –2 Page 3 of 7 VI. 3. Frontal 4. Temporal –2 5. Ethmoid 6. sphenoid G. 14 - Bones of the face 1. Nasal- 2 2. Lacrimal – 2 3. Zygomatic –2 4. Maxillae –2 5. Mandible 6. Turbinal –2 7. Vomer 8. Palatine –2 H. Bones of the Neck 1. Hyoid 2. Cervical vertebrae I. Bones of the Chest 1. Thorax 2. Sternum 3. Thoracic Vertebrae J. Bones of the Shoulder, Arm , Hand and Feet 1. Clavicle 2. Scapula 3. Humerus 4. Ulna 5. Radius 6. Carpus 7. Metacarpus 8. Phalanges 9. Tarsals 10. Metatarsals 11. Patella 12. Tibia 13. Fibula The Muscular System A. Covers, shapes and supports the skeleton B. Myology – study of the structure, functions and diseases of the muscles C. Muscular Tissue 1. Striated a. Striped b. Voluntary c. Controlled by will 2. Non-striated a. Smooth Page 4 of 7 VII. b. Involuntary c. Function automatically 3. Cardiac a. heart b. Not found anywhere else in the body D. Muscles of the Scalp 1. Epicranius 2. Occipitalis 3. Frontalis E. Muscles of the Eyebrow 1. Orbicularis Oculi 2. Corrugator F. Muscles of the Nose 1. procerus 2. Nasalis G. Muscles of the Mouth 1. Quadratus Labii Superioris 2. Buccinator 3. Caninus 4. Mentalis 5. Orbicularis Oris 6. Risorius 7. Triangularis H. Muscles of the Ear 1. Auricularis Superior 2. Auricularis posterior 3. Auricularis Anterior I. Muscles of the Neck – Platysma J. Muscles that attach the Arms to the body 1. Trapezius 2. Pectoralis K. Muscles of the Shoulder, Arm and Hand 1. Deltoid 2. Biceps 3. Triceps 4. Pronators 5. Supinators 6. Flexors 7. Extensors 8. Abductor 9. Adductor 10. Opponent The Nervous System Page 5 of 7 A. VIII. Controls and coordinates the functions of all other systems and makes them work harmoniously and efficiently B. Neurology – branch of anatomy that deals with the nervous system and its disorders C. Every square inch of the human body is supplied with nerve fibers D. Divisions 1. Central (Cerebro-Spinal) 2. Peripheral 3. Autonomic a. Sympathetic b. Parasympathetic E. Types of Nerves 1. Sensory 2. Motor 3. Mixed 4. Reflex – automatic response to a stimulus F. Nerves of the Head, Face and Neck 1. Fifth – chief sensory nerve of the face a. Trifacial b. Trigeminal 2. Infra-trochlear 3. Seventh – chief motor nerve of the face 4. Posterior Auricular 5. Temporal 6. Eleventh - affects muscles of the neck and back 7. Greater Occipital G. Nerves of the Arm and Hand 1. Ulnar 2. Radial 3. Median 4. Digital The Circulatory System A. Controls the steady circulation of the blood through the body by means of the heart and blood vessels B. Blood Vascular System – heart and blood for circulation of the blood C. Lymph Vascular System – consists of lymph glands and vessels through which the lymph circulates D. Heart 1. Pericardium 2. Vagus – 10th cranial nerve 3. Right/left atrium 4. Right/left ventricle 5. Valves E. Blood Vessels Page 6 of 7 F. IX. X. 1. 2. 3. Blood 1. 2. 3. Arteries Capillaries Veins Nutritive fluid circulating through the circulatory system 98.6 F/37 C Circulation of the Blood a. Pulmonary – from the heart to the lungs to be purified b. Systemic – from the heart throughout the body and back to the heart 4. Composition of the Blood a. Red corpuscles b. White corpuscles c. Blood platelets d. Plasma G. Lymph – Vascular System 1. Lymph – colorless, watery fluid derived from plasma 2. Primary functions of lymph H. Arteries of the Head, Face, and Neck 1. Facial 2. Common Carotid 3. Frontal 4. Parietal 5. Occipital I. Veins of the head, Face and Neck – Internal/External jugular J. Blood Supply for the Arm and Hand 1. Ulnar 2. radial The Endocrine System A. Glands – specialized organs that vary in size and function B. Exocrine 1. Duct glands 2. Sweat/Sudoriferous glands 3. Oil/Sebaceous glands C. Endocrine 1. Ductless glands 2. Pancreas glands 3. Thyroid glands 4. Adrenal glands 5. Pituitary gland The Excretory System A. Purifies the body by eliminating waste matter B. Kidneys C. Liver Page 7 of 7 XI. XII. D. Skin E. Large Intestine F. Lungs The Respiratory System A. Diaphragm B. Lungs – spongy tissue composed of microscopic cells that take in air C. Inhalation D. Exhalation E. Nose breathing healthier than mouth breathing The Digestive System A. Process of converting food into a soluble substance B. Digestive Enzymes