Human Anatomy 11 Body Systems
advertisement

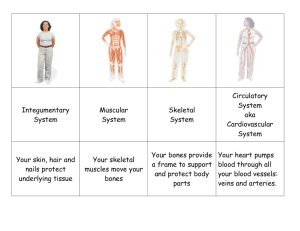
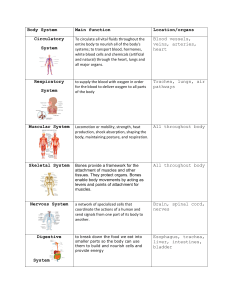
Human Anatomy 11 Body Systems Human Anatomy There are 11 systems that interact to make-up the human body and its functions. The most commonly know systems are the Skeletal, Muscular, Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Nervous, Reproductive, and Digestive systems. The others are the Integumentary, Endocrine, Immune, and Excretory systems. Skeletal System Consists of Bones and Joints Major function is to provide the body with support and protection. Divided into Axial and Appendicular sections. Muscular System Consists of muscles, tendons and ligaments. Three types of muscle. Skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. Tendons connect muscles to bones. Ligaments connect bones to bones. Cardiovascular Consists of heart, blood vessels and blood. Heart has four chambers. Three types of blood vessels; arteries, veins and capillaries. Respiratory System Major organs are lungs and bronchi. Functions as bodies gas exchange system. Provides cells with oxygen. Removes carbon dioxide. Nervous System Consists of Brain, Spinal Chord and nerves. Controls both somatic and autonomic body functions. Reproductive System Consists of male and female reproductive organs. Organs in the body responsible for producing gametes. Female organs able to support the growth and development of a fetus. Digestive System Major organs are esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, and colon. Breaks down food into molecules that the body can use for energy and other functions. Integumentary System Skin, hair and nails. Controls body temperature. Protects the body from outside dangers (bacteria, disease, temperature, etc.). Endocrine System Made up of a series of glands. Produce the hormones that regulate body growth and development. Immune System Consists of glands and lymph nodes. Filter blood and remove harmful substance from the body. Excretory System Consists of kidneys, ureter, and bladder. Removes urine from the body.