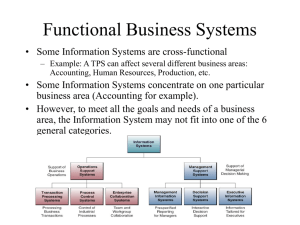
Types of Information Systems
advertisement
Types of Information Systems: Ways to Use IT in Organizations MIS 320 Kraig Pencil Summer 2014 PPT Slides by Dr. Craig Tyran A. Game Plan • Introduction • Basic functions of IS • Types of information systems – – – – TPS … MIS … DSS … ES … Office automation systems Functional Area Information Systems And more ! PPT Slides by Dr. Craig Tyran B. Information Systems Knowledge 1. Who cares? • Useful for a manager to become familiar with the range of capabilities of IS If you want to use all the tools available in your profession, you need to know what IT tools can do … and cannot do … for you. If you want to effectively use IT in the workplace, you need to know how to work with IT. • Consider a golfer and his/her golf clubs … Know what is in your bag! … And how to play the shots! Reality check: Some “trouble shots” are tougher than others ! Even a good golf club – or IS – may not be able to work miracles. Alphabet Soup Alert !!! Image source: http://codyfrew.wordpress.com/2007/06/29/acronyms-friends-or-foes/ B. Information Systems Knowledge 1. Who cares? (cont.) • Managers need to be aware of what people in the workplace are talking about when they hear names/acronyms such as … TPS. MIS, DSS ERP. SCM, CRM C. Basic Functions of Information Systems: The 5 Cs of Information Processing What do information systems do? 1. Capture: Obtain info at its point of origin 2. Cradle: Store info 3. Create: Process info to obtain new info 4. Convey: Present info in a useful form 5. Communicate: Deliver info to others PPT Slides by Dr. Craig Tyran and Kraig Pencil D. Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) 1. What is a business “transaction”? – – – 2. Examples of TPS – 3. ??? TPS emerged in the early days of IS – – – 4. A business event worth capturing and storing Examples??? Always $$$ transactions? Perform routine, repetitive tasks Often stores data in a database The Sales TPS is probably the most common & critical Collect, store, and process transaction data Order Entry TPS D. Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) 6. Related expression: Online transaction processing (OLTP) – – What does “online” mean? How is this different from batch processing? 7. TPSs may be found in all functions (production, accounting, marketing, etc.) of an organization 8. Some TPSs are at the very heart of the organization • If a critical TPS fails, the whole organization may suffer – or even fail!!! TPS D. Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) TPS Functional Area IS (e.g. HR, marketing, etc.) Business Intelligence (to aid decision-making) Barcode scanner Interorganizational System TPS data are often fed to other systems Databases PPT Slides by Dr. Craig Tyran & Kraig Pencil Expert System Other systems: Dashboard, ERP, IOS, Web 2.0, etc. E. Management Information Systems 1. Provide people with useful information (hopefully!) • • 2. E.g., periodic summary reports, comparison reports Alternate name: “Management Alerting Systems” Beware! • Managers can get swamped with too many reports 3. A MIS typically uses information that has already been captured and cradled into a database • 4. Quick question: Which type of IS might collect the data? The key Cs: Create and Convey • See figure E. Management Information Systems Management Information System Management Information System E. Management Information Systems 5. You will learn how to create systems that help to transform data tables into more useful information • First half of quarter MS Access • Second half of quarter MS Excel MIS Example: Using Excel to transform a data table into a more useful form (PivotChart) – See Excel book: Tutorial 5 MIS Example: Using Access to transform a data table into a report – See Access book: Tutorial 4 DSS, also known as BI (Business Intelligence systems) F. Decision Support Systems (DSS) 1. 2. DSS are used to support un/semi-structured problems that require human judgment DSS typically allow user to interact with information and explore (e.g., “What if” analysis – see figure) Decision maker can modify sales, expense, & cost assumptions to explore impact on profit F. Decision Support Systems (DSS) 3. The key Cs: Create and Convey 4. DSS can come in many forms • Managers often use spreadsheet-based DSS • MIS 320 Excel experiences will be helpful! 5. Common components of a DSS (see figure) • • • User interface Model management Data management DSS: Paper Production Planning and Scheduling Models: Product demand forecast Capacity planning/scheduling Paper roll cutting Company Data Base Easy to use interface, Data charts, etc. Cash Flow Projection DSS PPT Slides by Dr. Craig Tyran G. Functional & Productivity Systems Functional Systems • • • • MSCM: Manufacturing Supply Chain Management CRM: Customer Relationship Management http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BMtv6sbmdLc PM: Project Management systems Finance/Accounting Office Automation Systems Email/chat, document sharing, meeting management, publishing, presentations … Examples: • Microsoft Office • Google Apps H. Later in the course … 1. InterOrganizational Systems (IOS) – – Play an important role in electronic commerce Support flow of information between a) an organization and b) business partners Example: Business-to-Business IOS (B2B) – • – – Supply chain management The key C: Communicate (deliver information) See figure on next slide Image source: http://www.ecybersolutions.com/commerce.html InterOrganizational System: Support linkages between organizations Which are the B2B “IOS” Linkages ?? Source: Rainer, Potter, and Turban, Intro to IS, Wiley, 2009. H. Later in the course … (cont.) 2. Enterprise Resource Planning systems (ERP) – Key focus is on the “E” word: Enterprise Resource Planning – Offers potential to integrate transaction information across all organizational departments and functions 3. Systems based on “Web 2.0” technologies – Examples of technologies • Weblogs (blogs), Wikis, Social networking – Purpose? • • Support web-based collaboration “Social computing” I. Identifying IT Opportunities ERP DSS “Web 2.0” Systems Functional and Productivity Systems MIS TPS Other types of IS IOS Consider the IS applications in your organization and ask yourself … • • In which categories do our applications fit? Are we missing out on opportunities to compete more effectively through new information technology?