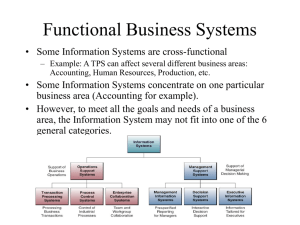
Businesses invest in IT to achieve six important business
advertisement

Businesses invest in IT to achieve six important business objectives Operational excellence New products, services, and business models Customer and supplier intimacy Improved decision making Competitive advantage Survival Three dimensions of information systems Organizations People Technology Information technology: The hardware and software a business uses to achieve objectives Information system: Interrelated components that manage information to Support decision making and control Help with analysis, visualization, and product creation Data: streams of raw facts Information: Data shaped into meaningful, useful form Activities in an information system that produce information: input processes output feedback Problem solving: 4-step process Problem identification Solution design Choice Implementation Typical organizational problems Outdated business processes Unsupportive culture and attitudes Political in-fighting Turbulent business environment ,change Complexity of task Inadequate resources Typical technology problems Insufficient or aging hardware Outdated software Inadequate database capacity Insufficient telecommunications capacity Incompatibility of old systems with new technology Rapid technological change Typical people problems Lack of employee training Difficulties of evaluating performance Legal and regulatory compliance Work environment, ergonomics Poor or indecisive management Lack of employee support and participation ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ Four basic business functions Manufacturing and production Sales and marketing Finance and accounting Human resources Systems from a Functional Perspective Sales and marketing systems Manufacturing and production systems Finance and accounting systems Human resources systems Systems from a Constituency Perspective Transaction processing systems TPS Executive support systems ESS Management information systems MIS Decision support systems DSS Five basic business entities * Suppliers * Customers * Employees * Invoices/payments * Products and services TPS،، Major source of data for other systems ESS ،، Primarily a recipient of data from lower-level systems DSS ،، Use internal information from TPS and MIS في المقارنة TPS = serve operational managers ESS = Serve senior managers DSS & MIS = Serve middle managers E-business Use of digital technology and Internet to drive major business processes E-commerce Subset of e-business Buying and selling goods and services through Internet E-government: Using Internet technology to deliver information and services to citizens, employees, and businesses Enterprice Applications Enterprice systems supply chain management systems Customer relationship management systems Knowledge management systems ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ Types of Computers PDAs, handheld mobile devices PCs Workstation Servers Mainframes Supercomputer Grid computing Client/server computing Client : User point of entry Servers :Store and process shared data and perform network management activities IT infrastructure Computer hardware Computer software Data management technology Networking and telecommunications technology Technology services Primary secondary storage technologies Magnetic disk :Hard drives, USB flash drives RAID :Can package hundreds of drives for massage storage requirements Optical disks CD-ROM, CD-RW, DVD Magnetic tape Storage networking :SANs Connect multiple storage devices on a separate high-speed network dedicated to storage Operating System Software The software that manages and controls the computer’s activities Data warehouse Database that stores current and historical data that may be of interest to decision makers Input devices: Keyboard Computer mouse Touch screen Optical character recognition Pen-based input Digital scanner Audio input Output devices: Monitor Printer Audio output Information systems collect and process information in one of two ways Batch processing: Transactions stored for predefined amount of time ,then processed as group Online processing: Transactions processed immediately * Software packages and desktop productivity tools Word processing software Spreadsheet software ( Excel ) Data management software Presentation graphics Software suites Web browsers HTML ( Hypertext markup language) XML (extensible markup language) SOAP (simple object access protocol) WSDL (web services description language) UDDI (universal description, discovery, and integration) SOA ( Service oriented architecture ) TCO ( Total Cost of Ownership ) SaaS ( Software as a Service ) Scalability : Ability of system to expand to serve large number of users without breaking down . ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ Logical view: How end users view data Physical view: How data are actually structured and organized Examples of DBMS: Microsoft Access, DB2, Oracle Database, Microsoft SQL Server, MYSQL . SQL ( Structured query language ) Tools for analyzing, accessing vast quantities of data: Data warehousing Multidimensional data analysis Data mining Utilizing Web interfaces to databases Types of information obtainable from data mining Associations: Occurrences linked to single event Sequences: Events linked over time Classifications: Patterns describing a group an item belongs to Clusters: Discovering as yet unclassified groupings Forecasting: Uses series of values to forecast future values Poor data quality: Major obstacle to successful customer relationship management Data quality problems: Caused by Redundant and inconsistent data produced by multiple systems Data input errors Data quality audit: Structured survey of the accuracy and completeness of data Data cleansing: Detects and corrects incorrect, incomplete, improperly formatted, and redundant data . ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ What Is a Computer Network? Two or more connected computers . Major components in a simple network Client computer Server computer Network interfaces (NICs) Connection medium Network operating system Hub or switch Routers : Device used to route packets of data through different networks, ensuring that data sent gets to the correct adder . The Internet: Largest implementation of client/server computing . Protocols: Rules that govern transmission of information between two points. • Four layers • • • • Application layer Transport ayer Internet layer Network interface layer LANs ( Local-area networks ) CANs ( Campus-area networks) Peer-to-peer Topologies: star, bus, ring WANs MANs RSS URLs ( Wide-area networks ) ( Metropolitan-area networks) (Really Simple Syndication) ( Uniform resource locators ) Physical Transmission Media • Twisted wire (modems) • Coaxial cable • Fiber optics and optical networks • Wireless transmission media and devices • Transmission speed (hertz, bandwidth) Hotspots: One or more access points in public place to provide maximum wireless coverage for a specific area . 5