Management Information Systems
advertisement

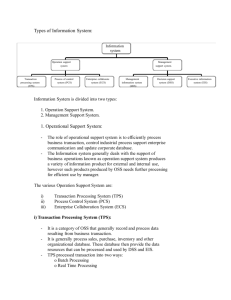
Management Information Systems CS208 Information System Overview An information system is a collection of people, procedures, software, hardware, and data Having sufficient information is crucial to an organization’s success Computers can collect information and then use that information to help people make decisions Management Levels Top-level managers - responsible for strategic planning -- need highly summarized information Mid-level managers - responsible for tactical planning -- need partially summarized information Supervisors - responsible for operational matters -- need detailed day-to-day information Information Flow by Management Level Information needs are based on the level of management Top level management Strategic: future-oriented Information summaries from both internal and external sources Flow is up and from outside Information Flow by Management Level Middle management Tactical: Historical Summarized weekly or monthly information from internal sources Flow is horizontal and vertical across functions Supervisors Operational: day-to-day Detailed information from internal sources Information flow is primarily vertical Computer-Based Information Systems There are four kinds of computer-based information systems: Transaction Processing Systems Management Information Systems Decision Support Systems Executive Information Systems Transaction Processing System (TPS) Performs routine transactions necessary to conduct business. Records day-to-day transactions (operations) in a database Maintains foundational data for the other information systems File and Methods used in Transaction Processing Files Used: Master File – Permanent data records Transaction File – Holding file that contains transactions (additions, deletions, and revisions) to be applied to the master file. Methods Used: Batch Processing – Transactions are collected over time and then processed all at once, as a “batch” to update the master file. Online (Real-time) Processing – Each transactions is used to update the master file immediately. Management Information Systems (MIS) Collects and analyzes data from all departments. Produces standardized reports in summarized, structured form Designed to provide an organization's middle management with up-to-date information (such as financial reports, inventory, etc.) at any time. Unlike transaction processing systems, which create databases, the MIS uses databases DBMS is required to integrate data across functional areas MIS Common Report Categories Periodic - regular intervals, pre-determined format, consistent content Exception - highlight unusual events Demand - as opposed to periodic, only upon request Decision Support System (DSS) Helps provide answers to unexpected, nonrecurring problems Produces summaries of large amounts of data, filtered and synthesized to support strategic nonroutine, decision-making Combines data from TPS with analytical models or data analysis tools Uses communications technologies, data, documents, knowledge and/or models to complete decision process tasks. Sample DSS Analyses Sensitivity Analysis What-if Analysis Study of effect that changes in one or more parts of a model have on other parts of the model Checks impact of a change in the assumptions or other input data on the proposed solution Goal-seeking Analysis Finds the value of the inputs necessary to achieve a desired level of output Executive Information System (EIS) A special type of DSS that presents data so that it is easy to use by top executives without extensive training. Provides corporate information, such as financial condition and market share, usually presented graphically so executives retrieve information by pointing to objects on the screen. Has drill-down capability and access to key external data. Executive Information System (EIS), continued Information is presented in a very aggregate form so executives can quickly scan it for trends and anomalies Addresses unstructured decision making through advanced graphics and communications. Sourced both internally from TPS and MIS and from external sources Gives senior management a broad company view, assists with strategic planning Information Systems Summary TPS Repetetive Linear Logic Regular Reports No Decision Support MIS DSS EIS Specialized Heuristics Complicated Logic No Regular Reports Supports Decision Making