Hi Grade 12s, As you can tell, I've completely lost my voice. So I
advertisement

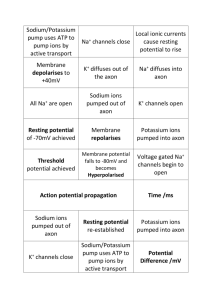
Hi Grade 12s, As you can tell, I’ve completely lost my voice. So I need you to do some silent work today unless you have questions. Should you have any questions, please come up to the front and ask me. I’ll whisper =) A. Circulatory System 1. What is the function f the heart? List the 3 types of blood vessels and give their functions. 2. Why are capillaries the most important part of a closed circulatory system? 3. State the functions of the valves found in veins. 4. Name the 2 atrioventricular valves. Where are they found? Give their function. 5. Trace the path of blood in the heart, listing all the chambers and valves. 6. Why is the heart said to be a double pump? 7. Why are the walls of the left ventricle so thick? 8. Define systole and diastole. How long does the cardiac cycle last? Atrial systole? Ventricular systole? 9. What is the lub heart sound due to? The dub heart sound? Define a heart murmur. 10. Why is the SA node said to be the pacemaker of the heart? the capillaries? 11. List 2 factors that contribute to the flow of blood through the venules and veins to the heart. 12. What is the difference between the pulmonary circuit and the systemic circuit? Contrast the pulmonary arteries and veins as to the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide present in them. 13. Trace the systemic path of blood to and from the kidneys. 14. What are the 3 major functions of blood? 15. If blood is prevented from clotting and placed in a test tube, what are the 2 major components? Give the percentage of the total volume of each fraction. 16. Define anemia. 17. How do leukocytes (WBC’s) differ from RBC’s? 18. Why does water exit a capillary at the arterial end? Tissue fluid consists of what components? 19. Why is water pulled back into the capillary at the venous side of the capillary? Where does the excess tissue fluid go? 20. Define an antigen. Where are antigens found? 21. Define an antibody. Where are antibodies found? What forms the antibodies? 22. What antigens are found on RBCs for blood type O? What antigens are found in the blood? B. Respiratory System 1. List the three things that happen to air (and how it is achieved) as it moves along the passages. 2. What are oxyhemoglobin and carbaminohemoglobin? How do they form? What is their role in the transport of gases in the blood? 3. Describe the concentration of O2 and CO2 in the umbilical vein and umbilical artery and explain why the concentrations are different. C. Nervous System 1. 2. 3. 4. What are the 2 main divisions of the nervous system? What do they include? What are the 3 main parts of all neurons? Distinguish between an axon and a dendrite. What is meant by the resting membrane potential? What is its value? Is it positive or negative? Describe the distribution of sodium and potassium ions on either side of the axomembrane. What is this unequal distribution of ions due to? In which direction will the ions be pumped? 5. Why are there always more positive ions outside the axomembrane than inside? 6. What contributes toward the negative charge in the axoplasm? 7. Why is the speed of conduction much faster in myelinated fibers than unmyelinated nerve fibres? What is this type of conduction called? 8. During the upswing of the action potential, what ion will flow into the axon? What happens to the charge on the inside of the axon? What is this termed? Hi Grade 12s, As you can tell, I’ve completely lost my voice. So I need you to do some silent work today unless you have questions. Should you have any questions, please come up to the front and ask me. I’ll whisper =) A. Circulatory System 23. What is the function of the heart? The function of the heart is to supply oxygenated blood to the whole blood and pump deoxygenated blood to the lungs to get re-oxygenated. List the 3 types of blood vessels and give their functions. Arteries, veins and capillaries 24. Why are capillaries the most important part of a closed circulatory system? They are important because that is the location where gas exchange happens. 25. State the functions of the valves found in veins. Valves are present in veins to prevent blood from back flowing due to gravity and to help blood travel toward to the R.A. 26. Name the 2 atrioventricular valves. Tricuspid and Bicuspid. Where are they found? Found between the left atrium and ventricle and right atrium and ventricle. Give their function. They prevent blood from flowing from the ventricles into the atria. 27. Trace the path of blood in the heart, listing all the chambers and valves. LA AV RV SL aorta body inferior(lower body)/superior (head) vena cava RA AV RV SL pulmonary trunk pulmonary artery lungs LA 28. Why is the heart said to be a double pump? Because there are two systems: the pulmonary and systemic systems. 29. Why are the walls of the left ventricle so thick? The left ventricle is the chamber responsible for pumping blood to the entire body. Therefore, it needs strong and thick muscles to achieve that. 30. Define systole and diastole. Systole is the contraction of the heart muscle and diastole is the relaxation. How long does the cardiac cycle last? 0.85 sec Atrial systole? Contraction of the atria Ventricular systole? Contraction of the ventricles 31. What is the lub heart sound due to? Lub is the first sound that the heart makes. It is caused by the closing of the AV close after blood passes through it. The dub heart sound? The dub sound is the second part of lub-dup. It is caused by the closing of the SL valve. Define a heart murmur. A heart murmur occurs when the valves don’t close properly causing the blood to backflow into the atria and ventricles. This will change the normal sound lub-dup to a “murmur” 32. Why is the SA node said to be the pacemaker of the heart? The SA node is said to be the pacemaker because it initiates the first electrical signal in the cardiac cycle. the capillaries? 33. List 2 factors that contribute to the flow of blood through the venules and veins to the heart. There’s only one important one – Valves and the muscles that move the valves 34. What is the difference between the pulmonary circuit and the systemic circuit? Contrast the pulmonary arteries and veins as to the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide present in them. (I’m not answering this question anymore. You should know by now =)..) 35. Trace the systemic path of blood to and from the kidneys. Aorta renal artery kidney renal vein inferior vena cava heart 36. What are the 3 major functions of blood? 1. Regulate 2. Transport 3. Protect 37. If blood is prevented from clotting and placed in a test tube, what are the 2 major components? 1. Plasma 55% 2. platelets and leukocytes ~1% 3. RBC 45% Give the percentage of the total volume of each fraction. 38. Define anemia. When there isn’t enough RBCs in the blood therefore the person feels tired due to lack of O2. 39. How do leukocytes (WBC’s) differ from RBC’s? RBC WBC No nucleus With nucleus Small Big One type Various types Carried O2 and CO2 Fights infections Shape = biconcave Various shapes 40. Why does water exit a capillary at the arterial end? Water exit the capillaries at the arterial end because the blood pressure is stronger than the osmotic pressure at the arterial end. Therefore it forces materials in the blood out of the capillaries. Tissue fluid consists of what components? (O2, CO2, nutrients, proteins, amino acid, metabolic wastes) 41. Why is water pulled back into the capillary at the venous side of the capillary? Because the osmotic pressure is higher at this point therefore it is “pulled” or “pushed” back into the capillaries. Where does the excess tissue fluid go? Into the lymphatic system, into the lymph 42. Define an antigen. Where are antigens found? An antigen in the circulatory system is found on the RBC. An antigen is any substance to which the immune system responds 43. Define an antibody. Where are antibodies found? What forms the antibodies? Antibodies are Yshaped proteins produced to protect the body from foreign invaders. Antibodies are able to recognize antigens and bind to it to disable it. It is found in the blood plasma. WBC makes antibodies. 44. What antigens are found on RBCs for blood type O? What antigens antibodies are found in the blood? There are no antigens found on the RBCs of type O blood. But there are Type A and B antibodies found in the blood of someone with Type O blood. B. Respiratory System 1. List the three things that happen to air (and how it is achieved) as it moves along the passages. a. filtered: nose hairs remove large particles, mucus traps smaller dust particles b. moistened: the air is moistened by the mucus surrounding the resp. tract c. Warmed: air is warmed by the body heat 2. What are oxyhemoglobin and carbaminohemoglobin? They are the name for hemoglobin when they are attached to oxygen and carbon dioxide. How do they form? They are formed at the RBC where the hemoglobin is located. O2 attaches to Hb when the pH is around 7.4 and temperature is warm (38C). What is their role in the transport of gases in the blood? Hb carries these gases so that they can be absorbed by tissue cells 3. Describe the concentration of O2 and CO2 in the umbilical vein and umbilical artery and explain why the concentrations are different. Umbilical vein = high in O2 and Umbilical artery = high in CO2. The difference is created by the blood that they contain. The umbilical vein carries blood from the placenta to the fetus and the umbilical artery carries blood from the fetus back to the placenta. C. Nervous System 1. What are the 2 main divisions of the nervous system? What do they include? CNS and PNS – CNS includes the brain and spinal cord. PNS includes the cranial and spinal nerves. 2. What are the 3 main parts of all neurons? Dendrite, cell body, axon Distinguish between an axon and a dendrite. An axon is the part of the neuron that takes electrical signals AWAY from the cell body. The dendrite is the part of the neuron that takes electrical signals TO the cell body. 3. What is meant by the resting membrane potential? Resting potential means when there is NO IMPULSE travelling through the neuron. What is its value? -65mV. Is it positive or negative? negative 4. Describe the distribution of sodium and potassium ions on either side of the axomembrane. Cl- and K+ on the inside of the axon. Na+ on the outside of the axon What is this unequal distribution of ions due to? Unequal distribution is caused by the constant leak of ions through the Na+/K+ pump. In which direction will the ions be pumped? Pumps always transport Na+ out and K+ in. Therefore there’s always more Na+ on the outside and more K+ on the inside. 5. Why are there always more positive ions outside the axomembrane than inside? Because of the pump. Read answer #4 above. 6. What contributes toward the negative charge in the axoplasm? K+ 7. Why is the speed of conduction much faster in myelinated fibers than unmyelinated nerve fibres? Myelinated fibers allow the impulse to “jump”. If the axon was unmyelinated the impulse has to travel the entire length of the axon BUT if it was myelinated, the impulse only has to travel a portion of the axon and “jump” over the other portions. What is this type of conduction called? Saltatory Transmission 8. During the upswing of the action potential, what ion will flow into the axon? During the action potential, the sodium gates open and allow the sodium gates to flow into the axoplasm. What happens to the charge on the inside of the axon? Changes to +40mV What is this termed? Depolarization during action potential