Nervous 1 orange
advertisement
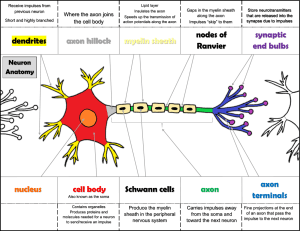
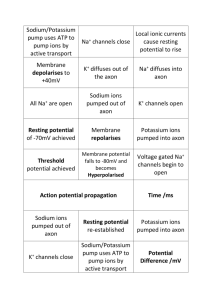
The Nervous System What Is A Motor Neuron? axon endings At Rest Inner • Dynamic equilibrium (1) Transport Proteins Stimulus • Threshold level (1) • Trigger zone (1) Action Potential • Sodium gated channels open • Depolarization • Sodium gates close • Potassium gates open • Repolarization • Sodium potassium pump restores gradient • (1,2) Travels down the axon like a crowd doing the wave (3) • Electric charge travels to the next set of protein channels (the next node), and triggers the gates to be opened. • The electric current moves down the axon of the cell. • The Myelin Sheath, made of insulating fat, quickens the process. • This jumping of electrical impulse between each sheath is called Saltatory Conduction (3). Overview (4). (skip to :29 then 2:18) MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS • • • • • Loss of control in speech, muscle control, and sight Loss of the myelin sheaths in the axon, or demyelination Lowers the rate of propagation Functions take much longer, if they ever happen (3). References (1). Star, Cecie, and Taggart, Ralph. Biology, The Unity and Diversity of Life. Pacific Grove, CA, 2001 (2). Bohan, Matthew. "Action Potential" President and Fellows of Harvard College and MCB-HHMI Outreach. 2005. Web. 3 Nov. 2010. <http://outreach.mcb.harvard.edu/animations/actionpoten tial.swf> (3). faculty.stcc.edu 2006 Springfield Techinical Community College 2006 <http://faculty.stcc.edu/AandP/AP/AP1pages/nervssys/unit11/sa ltator.htm> (4). garlandscience. "Action Potentials." Video. YouTube. 2009. Web. 5 Nov. 2010. <http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ifD1YG07fB8&feature =related>