Anatomy & Physiology 242 Cardiovascular System Objectives 1
advertisement

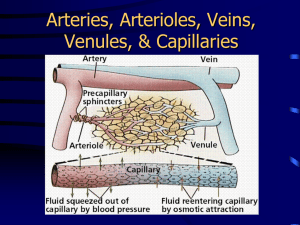
Anatomy & Physiology 242 Cardiovascular System Objectives 1. Describe the structure and function of each part of the heart including: the right and left atria, right and left ventricles, semilunar valves, tricuspid and bicuspid valves, chordae tendineae, papillary muscles, pulmonary arteries and veins, inferior and superior vena cava, and aorta. 2. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart and the vessels of the coronary circulation listing all structures and vessels by name. Explain why the right side of the heart is less muscular than the left side. Know the difference between the pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation. Explain how venous return is aided-muscular system, respiratory system and valves. 3. Describe how the 4 heart sounds are produced. 4. Describe the components of the heart's conduction system and how the system functions. Explain all parts of an EKG. Know what all deflections relate to during contraction of the heart and what changes in an EKG would reveal. 5. Explain how autorhythmic cells generate an action potential in the heart. What is sinus rhythm? What is responsible for sinus rhythm? How does the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems contribute to this rhythm. What does pacesetter mean? 6. Explain Starling’s Law. 7. Explain the action potential in cardiac muscle and relate it to ion changes. What causes the plateau? Why is it important in heart muscle? 8. Explain the nervous regulation of the heart-parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions. Know the neurotransmitters involved with each. Know which cardiac centers release them and what the consequences on heart rate, blood pressure, etc. are. 9. Explain how cardiac output and stroke volume are related. Know the formulas. 10. Know how various factors effect CO and SV. 11. Know how an action potential causes contraction of the heart. Be able to trace all the events of atrial & ventricular diastole and systole, include: isovolumetric contraction, ventricular ejection, EDV, ESV, stroke volume, ejection fraction, isovolumetric relaxation. 12. Know atrial & ventricular diastolic and systolic pressures. 13. Explain the relationship between vasodilation and vasoconstriction on blood pressure and blood flow to body areas. 14. Be able to explain flow rate and velocity of blood flow. Know how length, velocity and radius apply to both of these. Know the formulas. 15. Describe the structural and functional differences between arteries (elastic and muscular), capillaries, and veins. Explain in terms of their functions. Be sure to be able to give the location and structure of each of the tunicas. 16. Describe the distribution of blood in the arteries, capillaries, and veins. What does capacitance mean and refer to? Where is more of the blood stored? 17. Describe the different types of capillaries: continuous, fenestrated, sinusoids. Know where you would find them 18. Explain where peripheral resistance comes from, what it is, and how it influences blood flow and velocity of blood flow. Know all factors that affect peripheral resistance and how they affect it. 19. Explain how arterioles are regulated-nervous system and autoregulation. 20. Explain how materials are exchanged at the capillaries. 21. Explain the role of hydrostatic pressure, colloid osmotic pressure in capillary filtration and reabsorption. Know how CHP, IHP, BCOP and ICOP can be used to calculate NFP. What does this tell you about the direction of materials into and out of capillaries? 22. Explain how blood pressure is controlled including-nervous, hormonal and kidney regulation. 23. Know all hormones effecting cardiovascular regulation and know how they affect the heart. 24. Explain the significance of baroreceptors & chemoreceptors and how they regulate blood pressure. Know what stimulates each and the consequences of their stimulation. Know where they are located.