Properties of Matter 6.P.2.3
advertisement

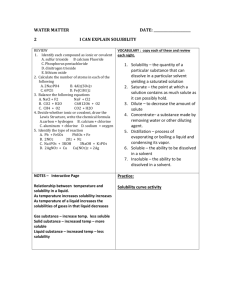
Comparing the Physical Properties of Pure Substances 6.P.2.3 Warm Up This is an example of matter; Can you identify it? How would you classify it? Think of ways scientists could classify different types of matter? Classification of Gold At room temperature: • Shiny • Hard • Does not dissolve in water • Does not smell (no odor) • Does not melt • Density = 19.3 g/cm3 • Melting Point = 1062 °C • Boiling Point = 2000 °C What is Characteristic Properties? Characteristic properties of matter are used by scientists to identify/ classify different substances Physical Properties: • Properties that can be measured and observed (no chemical change to the substance) • Includes: color, odor, density, solubility, melting point, boiling point Vocabulary • Classifyassign (someone or something) to a particular class or category. "elements are usually classified as metals or nonmetals" synonyms: categorize, group, rank, rate, order, organize, range, sort, type, • Physical Propertiesare used to observe and describe matter without changing its property. Ways to classify characteristic properties of matter • State of Matter: – solid, liquid, gas • Mass • Volume • Color • Odor • Density • Visibility: – Translucent, transparent, opaque • • • • • • Solubility Melting Point Boiling Point Dull/ Shiny Texture Flexibility Activity: Can you identify your original cookie? Density Volume Mass Weight How light or heavy something is because of its size. How much space an object takes up The amount of matter contained in an object. The force of gravity on an object It determines an objects ability to sink or float. Mass = Density Volume L x W x H= Volume or measure it with water with odd shaped objects It is measured in grams and ounces. It always stays the same. It always stays the same. Density Is a measurement of how tightly matter is crammed together. It tells you how light or heavy something is because of its size. Measuring Volume We will be using graduated cylinders to find the volume of liquids and other objects. Read the measurement based on the bottom of the meniscus or curve. When using a real cylinder, make sure you are eye-level with the level of the water. What is the volume of water in the cylinder? _____mL What causes the meniscus? A concave meniscus occurs when the molecules of the liquid attract those of the container. The glass attracts the water on the sides. Top Image: http://www.tea.state.tx.us/student.assessment/resources/online/2006/grade8/science/images/20graphicaa.gif Bottom Image: http://morrisonlabs.com/meniscus.htm What is the volume of water in each cylinder? Pay attention to the scales for each cylinder. Images created at http://www.standards.dfes.gov.uk/primaryframework/downloads/SWF/measuring_cylinder.swf Measuring Liquid Volume Measuring Solid Volume 9 cm We can measure the volume of regular object using the formula length x width x height. 8 cm _____ X _____ X _____ = _____ We can measure the volume of irregular object using water displacement. Amount of H2O with object = ______ About of H2O without object = ______ Difference = Volume = ______ Click here for an online activity about volume. Choose Lessons Volume & Displacement http://resources.edb.gov.hk/~s1sci/R_S1Science/sp/e n/syllabus/unit14/new/testingmain1.htm 10 cm Boiling Point Boiling and Melting Points • Boiling Point – The temperature at which liquid matter experiences the same pressure as the atmospheric pressure Freezing and Melting Points 32 ͦF/ 0 ͦC Physical changes can involve changes in energy. • Melting Point – The temperature at which solid matter turns to liquid • Freezing Point – The temperature at which liquid matter turns to solid Physical Changes • States of matter change (solid, liquid, gas) due to changes in energy / temperature Physical Changes • Boiling and freezing are physical changes that make the molecules of a substance move faster or slower and be closer or farther apart. • The molecules are not changed chemically! Physical Properties Physical Properties involve things that can be measured without changing the chemical properties Some factors that can change the characteristic properties of matter are heat, temperature, and pressure Physical Changes • Matter can undergo physical changes that only affect physical properties Example : wood cut in half both pieces still have the same physical properties Physical Properties of Matter • Solubility – The ability for a substance to dissolve Solutions, Solvents, & Solubility • Solution- is a mixture of substances • Solvent- is the part of the solution that is present in the greatest amount – The most common solvent is water. • Solutes-is the part of the solution that gets dissolved in the solvent Solvent + Solutes = Solutions Water + Sugar = Sugar Water SOLUBILITY • Solubility = the amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a given temperature • An important factor that influences solubility is the temperature of the solute and the solvent. • All things are not soluble Factors Affecting Solubility • The nature of the solute and solvent: different substances have different solubility • Temperature: many solid substances become more soluble as the temp of a solvent increases; however, gases are less soluble in liquids at higher temps. • Pressure: Only affects the solubility of gases. As pressure increases, the solubility of gases increases. Solutions sugar salt sand oil Vinegar copper sulfate Soluble or Insoluble? Observations Activity It looks as though none of the substance has disappeared It looks as if all or most of the substance has disappeared