WATER MATTER DATE: 2 I CAN EXPLAIN SOLUBILITY REVIEW
advertisement

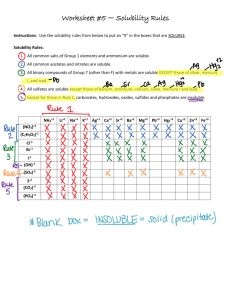
WATER MATTER 2 DATE: ______________________ I CAN EXPLAIN SOLUBILITY REVIEW 1. Identify each compound as ionic or covalent A. sulfur trioxide B calcium Fluoride C. Phosphorus pentachloride D. dinitrogen trioxide E. lithium oxide 2. Calculate the number of atoms in each of the following A. 2Na3PO4 B. 4Al2(SO4)3 C. 6PCl5 D. Fe(C5H5)2 3. Balance the following equations A. NaCl + F2 NaF + Cl2 B. CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2 C. CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O 4. Decide whether ionic or covalent, draw the Lewis Structure, write the chemical formula A.carbon + hydrogen B. calcium + chlorine C. aluminum + chlorine D. sodium + oxygen 5. Identify the type of reaction A. Pb + FeSO4 PbSO4 + Fe B. 2NO2 2O2 + N2 C. Na3PO4 + 3KOH 3NaOH + K3PO4 D. 2AgNO3 + Cu Cu(NO3)2 + 2Ag VOCABULARY : copy each of these and review each night. NOTES – Interactive Page Practice: Relationship between temperature and solubility in a liquid. As temperature increases solubility increases As temperature of a liquid increases the solubilities of gases in that liquid decreases Solubility curve activity Gas substance – increase temp. less soluble Solid substance – increased temp – more soluble Liquid substance – increased temp – less solubility 1. Solubility – the quantity of a particular substance that can dissolve in a particular solvent yielding a saturated solution 2. Saturate – the point at which a solution contains as much solute as it can possibly hold. 3. Dilute – to decrease the amount of solute 4. Concentrate– a substance made by removing water or other diluting agent. 5. Distillation – process of evaporating or boiling a liquid and condensing its vapor. 6. Soluble – the ability to be dissolved in a solvent 7. Insoluble – the ability to be dissolved in a solvent.