MYP UNIT: LIQUIDS /SOLIDS AND SOLUTIONS CHAPTERS 12
advertisement

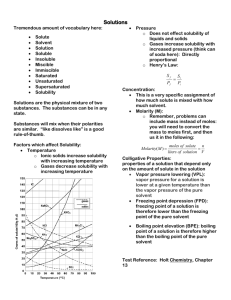
MYP UNIT: LIQUIDS /SOLIDS AND SOLUTIONS CHAPTERS 12-13 STANDARDS: 2.1.1, 2.1.3, 3.2.3 3.2.4, 3.2.5 & 3.2.6 I CAN: CHAPTER 12 Explain physical equilibrium: liquid water –water vapor. Explain that vapor pressure depends on temperature and concentration of particles in solutions Explain how energy (kinetic and potential) of particles of a substances changes when heated, cooled or changing phase Identify pressure as well as temperature as a determining factor for phases of matter Explain how temperature and kinetic energy are related Draw phase diagrams for water and carbon dioxide(show how sublimation occurs) Identify regions, phases and phase changes using a phase diagram Use phase diagrams to determine information such as (1) phase at a given temperature(2) boiling point and melting point at a given pressure (3) triple point of a material CHAPTER 13 Compute concentration(molarity) of solutions in moles per liter Calculate molarity given mass and volume of solution Calculate mass of solute needed to create a solution of a given molarity and volume Identify types of solutions (solid, liquid, gaseous, aqueous) Define solutions as homogeneous mixtures in a single phase Summarize colligative properties (vapor pressure reduction, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression and osmotic pressure Use graphs of solubility vs. temperature to identify a substance based on solubility at a particular temperature. Use graphs to determine degree of saturation of solutions to temperature Develop a conceptual model for the solution process as a cause and effect relationship involving forces of attraction between solute and solvent particles. ( a solution is insoluble because of a lack of attraction between solute and solvent.) Explain solubility in terms of the nature of solute and solvent attraction, temperature and pressure(for gases)