Functional Variety of Proteins
advertisement

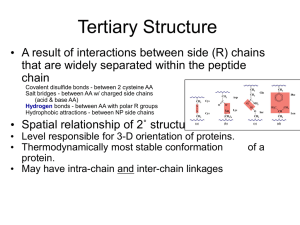
Functional Variety of Proteins Proteins: organic compounds containing carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N) and sometimes sulphur (S). What I need to know:1. Proteins are held in 3d shape 2. Proteins are held by bonds 3. Types of proteins and their functions Bonds in proteins 1. Peptide bonds Proteins are build up of sub-units called amino acids. These are joined together by chemical links called PEPTIDE BONDS. The sequence of amino acids determines the protein’s structure and function. The product – POLYPEPTIDE CHAIN (eventually a protein) AA1 AA2 tRNA tRNA U C G A G C A G C U C G A G G 2. Hydrogen bonds Weak hydrogen bonds form between amino acids in a polypeptide chain causing the chain to coil into a spiral. 3. Other linkages There are different cross-connections that bridges sulphur atoms with hydrogen bonds. These are important because they determine the final structure of the protein and so determine the function of the protein. They lead to the formation of FIBROUS or GLOBULAR proteins. Types of proteins A HUUUUGEEE amount of proteins exist in living things – the human body has 10,000 +. They are classified as either: Fibrous Globular Conjugated (Globular + non protein part) Fibrous proteins FIBROUS proteins are formed by several spiralshaped polypeptide molecules link together giving it a rope-like structure. Example: Collagen – found in bone providing inelastic, rigid support. Globular protein GLOBULAR proteins are formed with polypeptide chains fold into a spherical shape. This type of protein are vital for all living cells and perform many functions: Enzymes Structural proteins Hormones Antibodies . Conjugated proteins These proteins are globular but also consist of a non-protein chemical. Examples: GLYCOPROTEIN - made up of protein and a carbohydrate. For example, mucus that helps lubricate and protect parts of the body. HAEMOGLOBIN – pigment that transports oxygen in blood. Consists of the protein globin and haem (nonprotein containing iron). Protein function • You will have come across many proteins before and covered some of the many roles they undertake in living organisms. • Research one of the proteins listed below and complete its ID helicase keratin kinase oxytocin integrins phosphorylase tubulin insulin actin catalase antibody collagen porin elastin polymerase pepsin myosin cytochromes haemoglobin amylase Protein name Structure: __(globular/fibrous)__ Location: _____________________________ Function: _____________________________ _____________________________ ______________________________ Simple diagram of the protein itself or showing what it does. Glossary • CONJUGATED PROTEIN – a protein which has a non-protein component associated with it. Examples include glycoproteins, lipoproteins and haemoglobin. • FIBROUS PROTEIN – a protein which forms fibres and has a structural rather than enzymatic function. Examples include keratin and collagen. • GLOBULAR PROTEIN – a protein which folds to give a complex 3-D tertiary structure. Examples of these are enzymes, hormones and antibodies. • PEPTIDE BOND – The C-N bond linking two amino acids together.