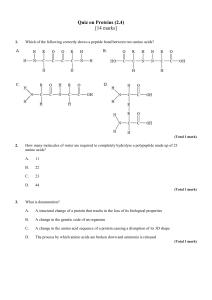
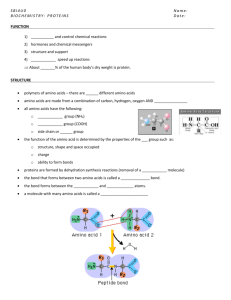
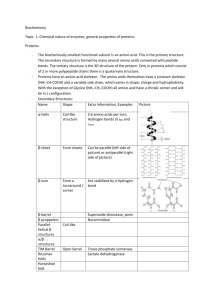
Protein Structure Worksheet: Biology & Chemistry
advertisement

EXPLORING PROTEIN STRUCTURE STUDENT WORKSHEET 1 By completing the set of activities designed for this task, you will revise and learn a number of the key knowledge areas assessed in VCE Biology and Chemistry. While working on this activity, prepare a glossary of the terms your teacher selects from the list on the final page of this worksheet. 1. Discuss the properties of the following fibrous proteins in relation to their structure and function: Collagen Fibroin Keratin 2. Some globular proteins, such as actin, can link together to form filaments. Discuss the importance of this property for cells. 3. Discuss how the microtubules of the cell cytoskeleton form. Relate this structure to the function of the cell cytoskeleton. 4. Enzymes are globular proteins that catalyse reactions in a highly specific manner. Discuss how catalase increases the rate of reaction for removing hydrogen peroxide from cells so it does not reach toxic levels. 5. Insulin, a globular protein, is released from cells in the pancreas in response to elevated levels of sugar in the blood, generally after eating. Insulin is a hormone, it travels in the blood to reach other cells and exerts its effect so they will absorb glucose and so liver 1 cells will store glucose as glycogen. What is the mechanism of hormone action for this protein (how does it trigger a response in other cells)? 6. Protein channels help to regulate the movement of specific molecules and charged ions across the cell membrane. The cell membrane has a hydrophobic (water-hating) interior. Would you expect to find the hydrophobic or the hydrophilic parts of a protein associating with the membrane? Explain. 7. Would you expect the interior of the protein channel to be hydrophobic or hydrophilic? Explain. Explain how antibodies bind to antigens in the humoral immune response. Discuss the specificity of this action. 8. To make proteins, cells copy the genetic code found on their DNA onto an RNA molecule. Name the macromolecule that reads the genetic code in RNA and briefly describe its mechanism of action. 9. What are the building blocks for making proteins? How many of these building blocks are involved in making proteins (how many blocks in the ‘protein building set’)? 10. Where does your body get the ‘building blocks’ for making proteins? 11. Give the general structure of an amino acid and discuss the R group. 12. Amino acids link together to form a polypeptide. What type of reaction leads to polypeptide production? 13. Draw the formation of a peptide from two amino acids and indicate the peptide bond. 2 14. Using diagrams &/or descriptors, describe the following: Primary structure Secondary structure Tertiary structure 15. What does the quaternary structure of proteins involve? 16. If a mutation in DNA causes a different amino acid to be joined to a growing protein chain, will this affect the shape of the protein? Explain. 3 TERM Structural DEFINITION TERM Amino acid DEFINITION protein Fibrous Residue Globular Condensation protein reaction Cell Peptide bond cytoskeleton Microtubules Polypeptide Bacteriophage Primary structure Enzyme Secondary structure Hormone Alpha helix Protein Beta sheet channel Ion channel Random coil Antibody Tertiary structure Epitope Hydrogen bond Antigen Disulfide bridge Gene Ionic bond Genetic code Conformation Codon Glycoprotein Ribosome Quaternary structure 4