Classwork - Biomonsters
advertisement
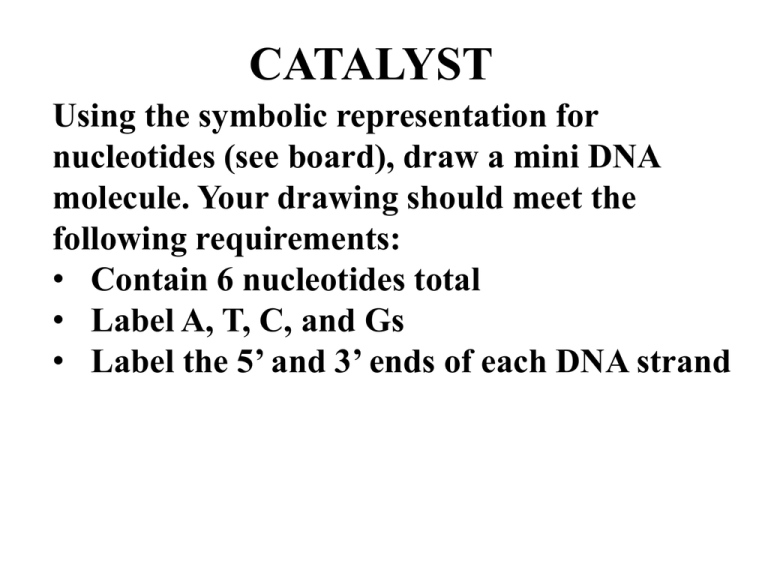
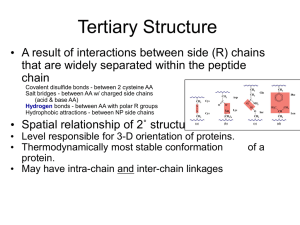
CATALYST Using the symbolic representation for nucleotides (see board), draw a mini DNA molecule. Your drawing should meet the following requirements: • Contain 6 nucleotides total • Label A, T, C, and Gs • Label the 5’ and 3’ ends of each DNA strand TODAY: PROTEINS! The Building Blocks of Proteins: AMINO ACIDS! R-groups affect Reactivity and Solubility Amino Acids as Buffers: How do Amino Acids Link Together to Form Proteins? Practice Peptide Bonding! 1. Draw two glycine amino acid molecules side by side (glycine’s R group is just “H” 2. Circle what atoms must be removed in order for a peptide bond to form 3. Draw the dipeptide that is formed DIRECTIONALITY! Protein Primary Structure Primary Structure Secondary Structure! Hydrogen bonding! Secondary Structure Tertiary Structure Tertiary Structure Quaternary Structure (in some proteins) Hemoglobin’s Chemical Formula: C3032H4816O872N780S8Fe4 Change in primary structure = Change in function! Mutated Cells Change in structure = Change in function! Change in structure = Change in function! Levels of Protein Structure – Group Demo Levels of Protein Structure In your group of 3 – 4 people… 1) Create a song / rap 2) Include all 4 levels of protein structure and the types of bonds / attractive forces involved in each level From 20 building blocks… A HUGE DIVERSITY OF STRUCTURE! Two Main Categories: 1) FIBROUS Structure: • Water insoluble • Very tough • Can be supple or stretchy • Parrallel chains in long fibers or sheets Two Main Categories: 1) FIBROUS Function: • Structural support - collagen in connective tissue • Contractile – actin and myosin in muscles Two Main Categories: 2) GLOBULAR Structure: • Water soluble • Tertiary / quaternary structure critical to function Two Main Categories: 2) GLOBULAR Function: Protective (antibodies) Two Main Categories: 2) GLOBULAR Function: Transport (aquaporins, hemoglobin) Two Main Categories: 2) GLOBULAR Function: Catalytic (enzymes) Two Main Categories: 2) GLOBULAR Function: Regulatory (hormone receptors) When Protein’s Go Awry = PRIONS! Normal Misfolded (Prion) • Scrapie • Kuru • Mad Cow Practice Free Response 10 points One of the unifying themes in biology is that function follows structure. Explain how the structure of proteins determines their function by responding to the following: Describe the structure of an amino acid (3) Outline the formation of a protein from its primary structure to its quaternary structure (4 points) Discuss the relationship between protein structure and function in fibrous and globular proteins (4)


![1. D [1] 2. A [1] 3. (a) sodium/Na 1 (b) unclear correlation between V](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010240645_1-d92b6d492f0c376ebcb72250f62b109a-300x300.png)