The End of Spanish Rule
advertisement

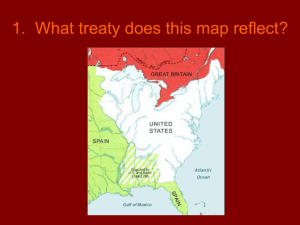
The End of Spanish Rule Chapter 6 1750 1800 1763: The Treaty of Paris ends the French and Indian War 1850 French and Indian War • Great Britain defeats France • Ended in 1763 by the Treaty of Paris • France’s North American lands divided between Great Britain and Spain – Great Britain gets land east of Mississippi River and Canada – Spain gets land west of Mississippi River and New Orleans • France is no longer a threat in North America French and Indian War – Treaty of Paris 1750 1800 1803: The United States buys Louisiana from France 1763: The Treaty of Paris ends the French and Indian War 1850 The Louisiana Purchase • 1800-Spain sold Louisiana back to France • 1803-France sold Louisiana to the United States for $15 million • The Louisiana Purchase doubled the size of the United States • Spain and America argued about the boundary The Adams-Onís Treaty The Sabine River became the eastern border of Texas The U.S. gave up all claims to Texas Finally, in 1819, the Adams-Onís Treaty settled the boundary dispute Spain ceded Florida to the United States 1750 1850 1800 1810: Mexican Independence Movement started 1803: The United States buys Louisiana from France 1763: The Treaty of Paris ends the French and Indian War The Call for Independence • The people of Mexico became unhappy with foreign rule – The best jobs were reserved for the Spanish, not the mestizos – Mexico paid for Spanish wars in Europe • September 16, 1810 – Father Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla issued a call, or grito, for independence • Father Hidalgo was executed after being caught The Gutierrez-Magee Expedition (Green Flag Rebellion) • Rebels from Mexico and the United States organized into the Republican Army of the North and declared independence for Texas • On August 18, 1813, an army of Royalists, or Spanish loyalists, ambushed the rebels south of San Antonio at the Battle of Medina • It was the bloodiest battle ever fought on Texas ground The Gutierrez-Magee Expedition (Green Flag Rebellion) • How bloody, you ask? – The republicans were annihilated – Those that weren’t killed and were caught and subsequently executed – About 1,300 of the 1,400 rebels were killed (that’s about 93%) – More than 40% of the population of Texas was killed in the battle – Only 55 Royalists were killed – The bodies of the republican rebels were left to rot for nine years before being allowed to be buried Effects of the Green Flag Rebellion • The Battle of Medina ended the Gutierrez-Magee expedition, but… – It was so disastrous that the battlefield has been lost because people would not talk about it – A Royalist lieutenant was recognized for his bravery in battle • It was there that he learned brutality and a take-noprisoners strategy from the Royalist Spaniards • He would go on to use that no-mercy strategy against rebels in Texas 23 years later in a mission in San Antonio • His name was… 1750 1850 1800 1810: Mexican Independence Movement started 1803: The United States buys Louisiana from France 1763: The Treaty of Paris ends the French and Indian War 1821: Mexico gains independence from Spain Mexico Gains Independence • The Mexican war for independence continued until 1821 • A disgruntled Royalist colonel named Agustín de Iturbide changed sides and was joined by armies across Mexico • In September 1821, Spain granted independence to Mexico – Texas became a province of • Agustín de Iturbide accepted the throne as emperor of Mexico Mexican National Anthem Mexicans, at the cry of war, prepare the steel and the steed, and may the earth shake at its core to the resounding roar of the cannon. Gird, oh country, your brow with olive the divine archangel of peace, for your eternal destiny was written in the heavens by the hand of God. But if some strange enemy should dare to profane your ground with his step, think, oh beloved country, that heaven has given you a soldier in every son. War, war without truce to any who dare to tarnish the country's coat-ofarms! War, war! Take the national pennants and soak them in waves of blood. War, war! In the mountain, in the valley, the cannons thunder in horrid unison and the resonant echoes cry out Union, Liberty! Oh country, 'ere your children defenseless bend their neck to the yoke, may your fields be watered with blood, may they trod upon blood. And may your temples, palaces and towers collapse with horrid clamor, and their ruins live on to say: This land belonged to a thousand heroes. Oh, country, country, your children swear to breathe their last in your honor, if the trumpet with warlike accent should call them to fight with courage. For you the olive branches! A reminder for them of glory! A laurel of victory for you! For them a tomb with honor! Mexicans, at the cry of war, prepare the steel and the steed, and may the earth shake at its core to the resounding roar of the cannon, and may the earth shake at its core to the resounding roar of the cannon! 1750 1850 1800 1810: Mexican Independence Movement started 1803: The United States buys Louisiana from France 1763: The Treaty of Paris ends the French and Indian War 1821: Mexico gains independence from Spain The Spanish Legacy • Spain ruled Texas for 300 years, but neglected it and there was little growth • Three settlements existed in Texas’ interior – San Antonio, Goliad, and Nacogdoches • What mark did they leave? – Many places and people have Spanish names – Roads were left behind – Spanish customs, like vaqueros and religious practices, helped form a distinctive Tejano culture