Unit Cells Practice test
advertisement

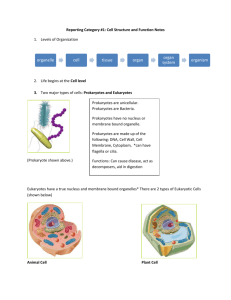
Name_______________________ due______________ Unit Cells Practice test This is NOT an actual test. You should NOT study from test review. Must study from notes, textbook, previous assignments/quiz, labs, research notes). Use notes (also available on my website) and/or textbook to complete this test review. Review organelle chart and label parts of organelle 1. Who first used the term “cells?” Hooke Who was the first person to identify and see cells? Leeuwenhoek Who concluded that all plants are made of cells - Schleiden Who concluded that animals are made of cells - Schwann Who studied cell reproduction - Virchow 2. What are the 3 things stated in the Traditional Cell Theory o living things are composed of one or more cells and cells come from existing cells by the process of cell reproduction o cells are the basic units of structure and function of all living things o cells contain specialized structures to perform functions necessary for life The Modern Cell Theory states the following 3 things (in addition to traditional cell theory) o Energy flow (metabolism and biochemistry) occurs within cells o Cells contain hereditary information (DNA) that is passed from cell to cell during cell division o All cells are basically the same in chemical composition in organisms of similar species 3. Differentiate between prokaryotes and Eukaryotes in the table below. Prokaryotes Eukaryotes 1. Do not contain memb bound organelle No nucleus 1.Contain memb bound organelle. Have nucleus. 2. metabolism in cytoplasm 2. Different parts perform different functions 3.simple smaller, mostly unicellular 3. complex larger mostly multicellular (exception Ex - Bacteria yeast amoeba) Ex. Higher animals plants 4.DNA is circular – present in cytoplasm 4. DNA linear – inside nucleus 4. What is common in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Cell memb, Ribosome, DNA, cytoplasm . 5. According to endosymbiotic theory, prokaryotes were engulfed by eukaryotes. Instead of getting digested they survived and function as which organelles - mitochondria, chloroplast. 6. What are the organelles that make proteins? Ribosomes 7. A cell with lots of ribosomes is probably specialized for protein synthesis. 8. The condensed strands of chromatin (the genetic material) of cells are called Chromosome 9. Which organelle converts food into compounds that the cell uses for energy? Mitochondria 10. Compared to a skin cell, a muscle cell is likely to have more Mitochondria (which organelle). 11. What is the main function of a cytoskeleton? 3D shape of the cell 12. Plant and animal cells both have Mitochondria. Plant cells have large vacuole, chloroplast, cell wall that animal cells do not have. Animal cells have lysosomes, centrioles that plant cells do not have. 13. A eukaryote having a nucleus, cell wall, chloroplasts and mitochondria would probably be a plant 14. An important difference between viruses & living cells are that viruses cannot reproduce outside of cells 15. What is the phospholipid layer of a cell that controls what enters and leaves the cell? cell membrane 16. The channels are embedded in the cell membrane that can move large polar molecules into and out of the cells. What are these channels made of? protein What kind of transport uses them? Facilitated diffusion, Protein pumps also use embedded proteins (active transport) 17. What is the diffusion of water called? osmosis 18. During diffusion, which way do the molecules move? high low Where do molecules move from during active transport? Low High 19. What kind of transport needs energy? active 20. What happens when a cell is placed into a hypertonic solution? Water leaves and shrinks What happens when a cell is placed into an isotonic solution? stays the same What happens when a cell is placed into a hypotonic solution? Water enters and swells 21. If an animal cell is surrounded by fresh water, what will happen to the cell? Burst (cytolysis) What kind of solution is fresh water for animal cell: hypertonic, isotonic or hypotonic? hypotonic 22. If a cell had a salt concentration of 10% inside it and it was placed in a 5% salt solution, what would happen to the cell? Swell What kind of solution is outside: hypertonic, isotonic or hypotonic. 23. Bulk transport/ Phagocytosis is active transport in which large molecules are packaged in membranebound sacs. Removal of material from cell is called exocytosis and taking material into the cell by means of infoldings is called endocytosis. 24. Bacteria and plants have cell walls and a protist like paramecium has contractile vacuoles that pump water out that prevents them from over-expanding. 25. The cells in multicellular organisms perform specific functions,that is called as cell _specialization. Give an example of cell specialization. Red Blood Cells 26. Blood is considered a tissue because it is composed of different types of Cells working together and having specific functions. 27. What determines cell shape? function 28. Starting with a cell and ending with an organ system, what are the four levels of organization in multicellular organisms? cells, tissue, organ, organ system 29. What would happen to the cell in each picture on the right?