II. Connective Tissue
advertisement

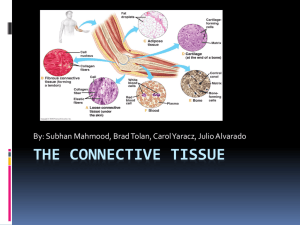
II. Connective Tissue Supports and 2 types of cells 1. Produces and maintains protects body parts intercellular material Manufactures blood which are composed of cells 3 types of protein fibers A. collagenous Composed of widely B. elastic scattered cells. Lie C. reticular within nonliving 2. protects tissue from material infection 3 Types of Protein Fibers Collagenous fibers (collagen) Elastic fibers (elastin) Reticular fibers (reticulum) 1. Collagenous Fibers (Collagen) Most abundant (10% total body weight) Thick wave like strands Flexible but tensile (resists stretching) Found in tendons (connect muscle to bones) Also used by body for tissue repair *scar tissue, binds skin tightly together 2. Elastic Fibers (Elastin) Not as strong as collagen Elasticity and extensibility * Pinch skin and it returns to its normal shape 3. Reticular Fibers (Reticulum) Resists physical stress Not abundant in connective tissue 4 Types of Connective Tissue Based on density of proteins) 1. Connective tissue proper 2. Cartilage 3. Bone 4. Blood-forming tissue and blood 1. Connective Tissue Proper Each type has a cell called fibroblast which produces the intercellular material 3 types based on the fibroblast a. Loose connective tissue b. Adipose tissue c. Dense connective tissue a. Loose Connective Tissue Most widespread Structural anchor to body parts Between skin and muscles Surfaces of organs Known as areolar tissue (referring to little area) b. Adipose Tissue Fat cells called adipocytes Fat stored as triglycerides Provides insulation and padding between organs c. Dense Connective Tissue Tightly packed protein fibers Regular or irregular Regular are fibers parallel to each other like tendons and ligaments (connect bones to bones) irregular are fibers not parallel like deep layers of skin (dermis) and external wrap around bones and cartilage. 2. Cartilage Harder than connective tissue proper Protein fibers in thickened gel-like ground substance called matrix Matrix maintained by “gristle” cells called chondrocytes that lie in small chambers called lacunae which get nourishment from the perichondrium (dense connective tissue) types of cartilage a.Hyaline b.Elastic c.Fibrocartilage a. Hyaline Bluish white Respiratory tract Ends of bones at movable joints Ends of ribs b. Elastic Yellowish Framework of ears End of nose Epiglottis (small opening to larynx) c. Fibrocartilage Thick collagenous fibers Joints like knees Between intervertebral discs (padded joints) QUESTIONS Packet pp.59-60 3. Bone Intercellular material is mineral salts and collagenous fibers Hardest and most durable of all tissue. Dense matrix Composed of matrix of osteocytes embedded in lacunae (chambers). Nourished by periosteum which is a membrane surrounding the bone. Canaliculi are channels through which nutrients reach bone cells 2 Types of Bone a. Compact bone b. Spongy bone b. Spongy Bone Not dense, have spaces called red marrow (blood forming tissue) Form thin plates called spicules Interior of bones Packet p.61 4. a.) Blood-Forming Tissue and 2 types b.) Blood a. Blood-forming tissue anufactures cellular components of blood Contains 3 components i. Stem cells (produce blood cells) ii. Young blood cells (newly formed) iii. Protein (lacks collagen, so is softest connective tissue) i. Red marrow Hematopoietic tissue (initiates production of all cells) ii. Lymphoid tissue In lymph nodes In tonsils Spleen, thymus Iit is maturation site of 2 types of W.B.C. 1. Lymphocytes 2. Monocytes b. Blood The WBC, RBC and platelets are called formed elements and are surrounded by a fluid matrix called plasma Formed elements means the fibers of the matrix are dissolved proteins Carries respiratory gases, nutrients and wastes Packet p. 62 Packet pages 57-62 should now be done Quiz on all notes through blood