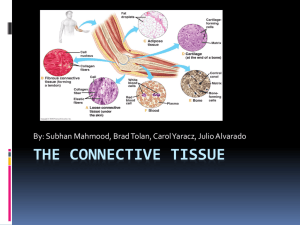
Connective Tissue Overview - TCHS Anatomy and Physiology
advertisement

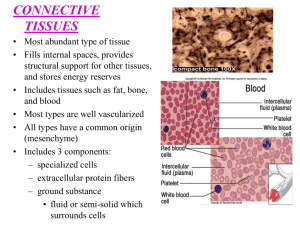
Name 2 types of epithelial tissue and their function. Connective Tissue Found everywhere in the body Includes the most abundant and widely distributed tissues Functions Binds body tissues together Supports the body Provides protection Insulates to maintain body temperature Transportation of other molecules 1. common origin- all arise from embryonic tissue (mesenchyme) 2. Degrees of vascularity- cartilage is avascular while other types have rich blood supply 3. Extracellular matrix- connective tissue more able to bear weight, withstand tension, and endure abuses because unlike other tissues it is not made up mostly of cells. Most abundant tissue in body 3 Main Elements Ground Substance: unstructured material that fills the space between the cells and contains the fibers. This is consists mostly of fluid and proteins. Fibers: provide support. • 3 types: collagen, elastic and reticular fibers. • • • Collagen fibers: protein. Extremely tough and provide high tensile strength. (white) Elastic fibers: long and thin that form branches. Elastin protein. Moves like a rubber band. (yellow) Found in skin, lungs, blood vessels. Reticular Fibers: very fine fibers that branch extensively. Surround small blood vessels and support tissue of organs. Cells- composed of many types 1. Blast Cells: undifferentiated cells -fibroblast - chondroblast -osteoblast -hematopoietic stem cells 2. Fat Cells- nutrient storage 3. Blood cells- defense 4. Plasma Cells-produce antibodies 5. Macrophages- dispose of dead tissue cells and act in immune response Connective Tissue Proper Loose (Areolar) Connective Tissue Adipose Tissue Dense Connective Tissue Fibers not abundant Extensive blood supply Examples of locations Between skin and muscles Around digestive tract Around blood vessels “Packing material” of body Still loose connective tissue Most of the volume is adipocytes Provides padding, slows heat loss, food reserve Locations Common under skin of sides, gluteal, and mammary regions Wherever there is loose connective tissue Lots of collagen fibers Examples Tendons (muscle bone) Ligaments (bone bone) Some has elastic fibers Cartilage Dense network of collagenous fibers & elastic fibers in a gel-like substance Avascular…repair capabilities limited Cells – chondrocytes in lacunae chondroblasts Perichondrium – surrounds surface of cartilage Most common Provides flexibility and support Locations Ends of bones larynx Trachea, embryonic skeleton Connecting ribs to sternum Visible collagenous fibers with scattered chondrocytes Provides strength and rigidity Locations Intervertebral discs Symphysis pubis Resilient and flexible External ear(pinna) Epiglottis Auditory tube Tolerates distortion without damage Bone (aka osseous tissue) Solid matrix (solid Ca cpds) Cells – Osteocytes in lacunae Osteoblasts Periosteum surrounds surface of bone Functions Transport medium Regulation Protection Composition Plasma – fluid Formed elements – cells & cell fragments Red blood cell White blood cell Platelets (important in clotting)