Medical Insurance
advertisement
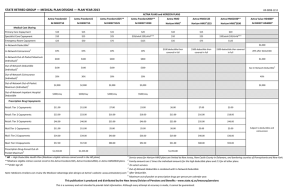
Medical Insurance Overview Many people in the US are uninsured – they assume all responsibility for health care costs. The number of uninsured is sizable and growing. Why??? Health insurance decreases the patients out of pocket expenses for health care services. How does insurance work? Insurance is more affordable when purchased in large groups – only a few of the insured will require constant medical care and use the insurance in large amounts. Co-insurance (i.e. 80%-20%). A percentage the patient is responsible for on a given insurance claim Companies purchase health insurance for employees Obtaining Health Insurance Coverage Through Your Employer Eligibility depends upon continuous employment Employees must work 20 or more hours per week at most companies. Most companies have a waiting period before insurance benefits are available (i.e. 30 days, 60 days, etc…). Pre-existing conditions may be ineligible for insurance coverage. Types of Health Insurance HMO - Health Maintenance Organization A type of managed care medical insurance Specialist treatment is available with a referral Insured are limited to contracted physicians for care. Out of pocket expenses are set. Specialty care must be submitted to HMO for approval – it may be denied. Types of Health Insurance PPO - Preferred Provider Organization Physicians contract services for a set fee and are listed as a preferred provider. The insured person chooses from a list of preferred providers. The insurance company pays a set amount and the insured pays a set amount called the co-payment. Referrals are made to specialists on the list. Types of Health Insurance Agency Plan Example: Aetna, Humana, Blue Cross/ Blue Shield, etc… Fees for insurance may be less up front Pay for larger portion of care when received May have large deductibles Usually more freedom in choice of doctors. Agency may offer several types of plans (HMO, PPO, etc…) Types of Health Insurance Medicare Government program providing health care to people over age of 65 and those who are disabled and have received Social Security benefits for at least 2 years. Medicaid Medical assistance program Operated by the STATE, not the federal government Pays for health care of people with low incomes, children who qualify for assistance, and people who are physically disabled or blind Types of Health Insurance • CHIP – Children’s Health Insurance Program – Controlled by the STATE. – Provides health care to uninsured children of working families who earn too little to afford private insurance but too much to be eligible for Medicaid. Worker’s Compensation Provides treatment for workers injured on the job and reimburses worker for lost wages (earnings) Controlled by the STATE Health Savings Accounts Health Savings Accounts (HSA) a type of medical savings account owned by an individual and is used to pay for current and future medical expenses. HSAs are commonly used in conjunction with a “High Deductible Health Plan” (HDHP). a health insurance plan with lower premiums and higher deductibles than a traditional health plan Health Savings Accounts High Deductible Health Insurance Minimum deductible $1,100 (self-only coverage) $2,200 (family coverage) Maximum out of pocket costs $5,600 (self-only coverage) $11,200 (family coverage) Optional Health Insurance Cancer Insurance Specific insurance for the treatment of cancers. In addition to basic health care insurance. Optional Health Insurance Disability Insurance Provides income upon disability – short or long term. Various waiting periods are available before benefits begin (12 weeks, pay 80%; 4 weeks, pay 60%, etc…) Optional Health Insurance Vision Insurance may pay a portion of an eye exam Some will cover the cost of glasses or contact lenses. Optional Health Insurance Dental Insurance covers a portion of teeth cleaning, fillings, x-rays, orthodontics and oral surgery Most of the time, there is a lifetime limit for orthodontic care Life Insurance Provides financial payment to a beneficiary in the event of death. Benefits can vary, depending on the needs of the family and individual. Employers often offer life insurance to their employees in the amount of the employee's annual salary. Individual policies can be purchased Types of Life Insurance Term Life Insurance – specific amount of money will be paid to a beneficiary. Whole Life Insurance – a policy that allows the holder of the policy to draw on the insurance as a pension, as well as having money go to a beneficiary at the time of death Let’s Practice….. You were injured while cheerleading at a football game and sustained a broken arm. The emergency department bill costs $489 to evaluate, x-ray, and apply a cast to your arm. The deductible is $100 on your health plan. Your insurance covers 80% of the costs (after the deductible is met) for the ER visit. How much will you pay out of pocket for the broken arm??? ER Visit Answer $489 total bill -100 deductible (you pay on arrival) $389 $389 x 80% $311.20 insurance company payment $389 -311.20 $77.80 additional amount you owe Let’s Practice some more… Find your 10 o’clock partner With your partner, complete the benefits packet including all of the math calculations. Determine how much money you would spend each payday on healthcare.