Virtual Patient PowerPoint
advertisement

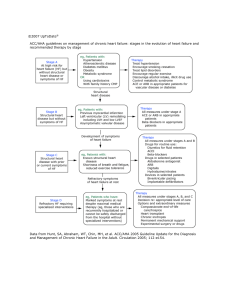
Provost’s ACIE Award A Novel Approach to Teaching The Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis Using Virtual Patient Technology Gary Tabas, MD University of Pittsburgh UPMC Shadyside Background • Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) – Associated with significant morbidity and mortality – Management involves complex decision making • LCME ‘educational gap’ – Only a minority of students will encounter a patient with DKA during ward rotation Liaison Committee for Medical Education. LCME considers proposed changes in accreditation standards. December 2006. Available at: http://www.lcme.org/hearing.htm. Current Educational Methods • Lecture • Small group discussion • PBL (Problem-based Learning) But management and decision making during direct patient care are often suboptimal. New Educational Approach Simulation would allow students to learn and practice DKA management skills in a safe environment Increasing role of simulation in student training recognized by LCME, ACGME Carnegie Foundation report - Educating Physicians: A Call for Reform of Medical School and Residency “Content of curriculum derived from patients seen” Project Goals 1. Implement a newly created web-based virtual patient (VP) simulation to teach the management of DKA. 2. Pilot test its effectiveness in teaching DKA-specific clinical decision making. 3. Assess students’ perceptions of the effectiveness of the DKA VP compared to other instructional methods. Virtual Patient Simulation • Virtual patients are computer-based simulations of medical cases for education and assessment Branched-Narrative VPs • Multiple pathways through the simulated case Pathway determined by learner’s management choices Consequence 1 Choice 1 Consequence 2 Vignette Consequence Choice 2 Learning with branched-narrative VPs • The learner acts as the practitioner who performs H&P, requests and interprets lab values and makes management decisions. • The learner sees the consequences of those decisions and adjusts management DKA Branched-Narrative VP • Diagnose DKA • Manage fluids, electrolytes, and insulin • Transition the patient from continuous IV insulin to subcutaneous insulin Methods Program Development • VP content sources – Diabetes Care 2006; Kitabchi A. – In The Clinic; Annals Int Med 2010 – Content review: Endo attending specializing in DM • Pretest/posttest: – Case-based; single best answer; NBME type aligned with teaching goals – Content review: Endo attendings and fellows • Survey: from literature; expert validation Learning Management system • VpSim created by the University of Pittsburgh Laboratory for Educational Technology • Flash-based visual interface • Author creates screens and management choices using a map of nodes and branches. • Adds patient data to each node. Better volume status Hypovolemic DKA patient Persistent hypovolemia Insulin & D5W Stop insulin Insulin & saline Insulin & D5W Track students' pathways through the case Track students' pathways through the case Advantages of VP Simulation • Exposure to rare patients • Incorporates adult learning theory: – Active engagement – Visualization/rehearsal (neurobiology of learning) – Adaptive learning (individualized instruction) – Self-reflection – Feedback (formative) Findings To Date Participants • 51 Third year medical students – AIMC • 84 pharmacy students – Clinical pharmacology course • 11 Endocrine fellows Pretest VP (path score, time-on-task) Posttest Survey Pre-Posttest Scores *P = .026 † P< .001 vs all posttest † Selected Posttest Questions Scores (%) † * NS * P = .01 † P<.001 VP Learning Path Score * P< .001 vs med students VP Time-On-Task * P = .004 vs other groups Correlations Outcomes *Correlation P value VP learning path score with posttest score .31 .0002 Time-On-Task with VP learning path score .21 .013 * Spearman’s ρ Survey Data The ability to see and react to the consequences of my decisions in this module was more effective in teaching me clinical decision making than with other learning methods All differences NS The module was effective in helping me learn how to adjust therapy in patients with DKA who are not responding appropriately * * P = .02 vs Med students The module improved my confidence in managing DKA. * * P = .01 vs other groups The module was of high educational value Summary • It is feasible to create a interactive branchednarrative VP to teach the management of a complex medical illness • One way to fill an educational gap • Effectiveness was significant as evidenced by pre-posttest score improvement • Students felt that the VP was effective in teaching management of DKA and preferred the VP over other teaching methods Limitations • • • • • • Expensive, time consuming Expertise Pilot study One case Two schools but in one institution No patient outcomes Future Research Compare effectiveness of branched-narrative VP to traditional VP with only one learning path Questions? Funding: University of Pittsburgh Provost’s Innovations in Education Award Acknowledgements: Harsha Rao Mary Korytowski Neil Benedict Mike Elnicki Dario Torre JB McGee Laboratory for Educational Technology The problem Insufficient insulin GLU ~16 ∆ ~15 ~200 HCO3 2 AM 4 AM 6 AM 8 AM 10 AM What do we know about the effectiveness of web-based education? • Superior to no intervention • Probably equal to non-internet education for knowledge gain • Superior to non-internet education for learning efficiency – (knowledge gained per time spent) • Superior for learning satisfaction Cook